Paper & Textile Industries
Dust Adhesion During Non-woven Fabric Cutting Process
Fabric is charged with static electricity in the transfer line. Static electricity is also generated by the friction between the fabric and blade during cutting, which makes fiber dust of the fabric float in the surrounding air.
The airborne fiber dust sometimes adheres to the fabric which is being transferred. Charged fiber dust adheres again even if it is removed with an air blow.
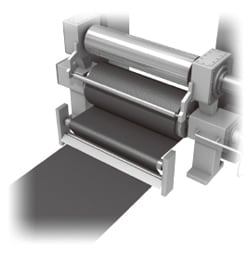
Conventional countermeasures
Conventional static eliminator
- The static elimination speed is insufficient.
Countermeasures with static eliminators (ionizers)
An ionizer provides an effective measure against foreign particles, which leads to a decrease in complaints.
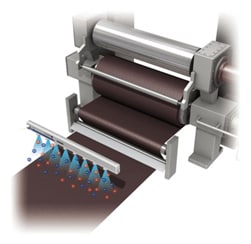
Improvements and Effects
Words from the worksite
Reduced cost for addressing defective products
Cost of recall and disposal of defective lots: $4,000/year
Recall cost (transportation and on-site service travel costs): $5,000/year
Cost of process improvement: $10,000/case