Measurement Sensors
Dimension Measurement
Displacement Measurement
Profile and Shape Measurement
Profile and shape measurements refer to quality manufacturing, quality control, and data acquisition processes that accurately capture the dimensions and contours of an object’s surface. As such, these systems are often paired with sophisticated data analysis software that compares measurement values against CAD models and provides detailed statistical quality control.
Applications associated with these processes include the production and quality control of small-scale components (such as microchips) up to large structures (such as aircraft components). This makes laser profiling and measuring shapes invaluable processes in the modern manufacturing environment.
When selecting a sensor for 2D measurements, the first step is to choose a method for generating a profile of the target. This can be performed by scanning a 1D sensor over a surface, using a laser line, or working from a 3D image. The target material, shape, and size will all play a role in determining the best fit. Check out some typical methods below, or request a free consultation with a measurement expert.
Choose Case of Profile and Shape Measurement
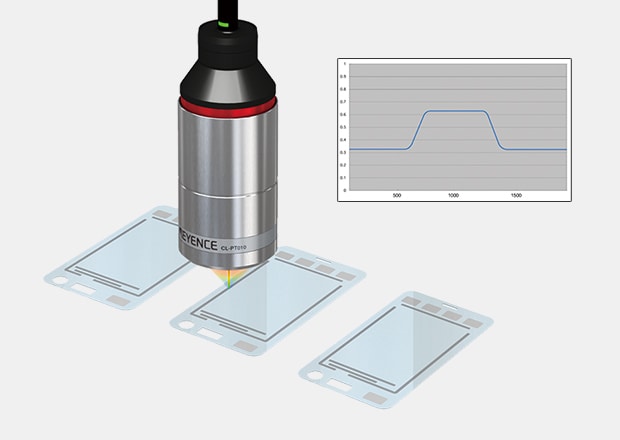
Electrode Shape Measurement of Touch Panel
Measure fine details on touch panels regardless of surface finish with confocal sensors. With a beam spot of 3.5µm, even the smallest features can be measured.
Tire Tread Shape Measurement
Profile tire treads and sidewalls with multiple 2D laser profilers.
Step Measurement After Etching
Measure the step height of features on a wafer after etching. With 3D interferometry, mirrored surfaces can be measured accurately.
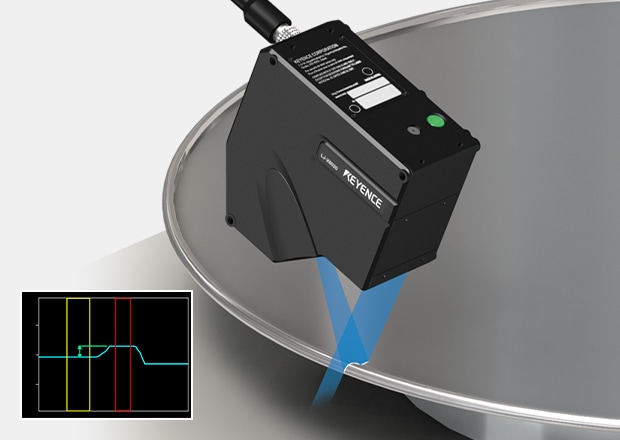
Shape Measurement of Balloon
Using 2D thrubeam sensors, medical balloons can be inspected inline at high speed.
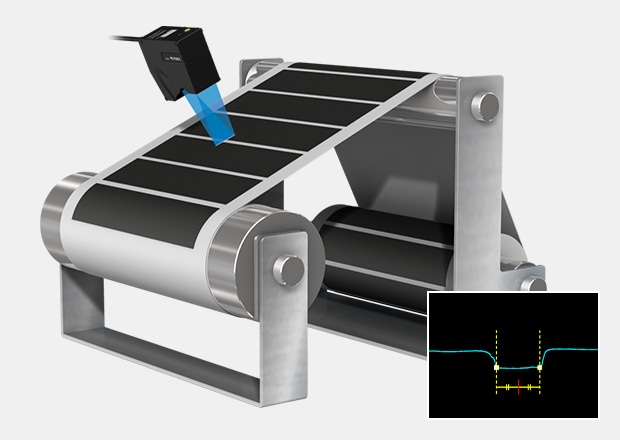
Inspection of Irregular Electrode Winding
Inspect for lamination misalignment after winding. With a minimum X-resolution of 2.5 µm 0.000098", the LJ-X8000 Series accurately measures the profile of each electrode.
Inspection of Disconnected Electrode Locations
Provide feedback about disconnected locations in electrodes before lamination. Accurately acquire the profile of electrode terminals to perform high-accuracy inspection of edge locations.
Wafer Edge Profile Measurement
Measure the profile of a wafer edge. By selecting one of the inspection tools, such as Height Difference/Width or Angle, users can start measurement easily. The high-resolution image capturing using 3200 points/profile achieves highly accurate profile measurement that was impossible with conventional methods.
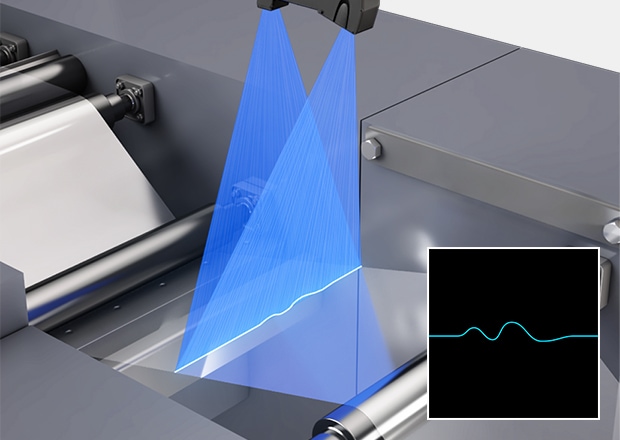
Film Curvature and Wrinkle Detection
Film curvature and wrinkling measurements are performed using a blue laser with a maximum width of 720 mm. Measurement is possible even for transparent targets thanks to the wide dynamic range of the CMOS sensor.
What is Profile Inspection?
A laser profile inspection is a simple and more cost-effective alternative to pricey vision systems, and they can be used to verify the presence of vital components, identify surface defects, and detect incorrect assemblies or warpages in flat parts.
As such, profile inspection ensures that manufactured parts and components are within specified tolerances and that they’ll fit together properly during final assembly.
Profile Measurement Sensors
Profile measurement sensors previously relied on contact profilometers, which were used to measure vertical displacement. However, newer technologies involve coordinated measuring machines (CMMs) that use contact probes to touch various points to create a profile.
Alternatively, modern solutions require non-contact sensors, which are great for measuring fragile objects or objects sensitive to touch. These systems employ displacement lasers or white light to scan a surface and compute a profile of a recorded object.
Profile Measurement Applications
As stated above, profile measurement is used across a wide variety of industries for monitoring part or seal presence, part and seal locations, as well as assembly flatness, tolerance stack-up, and surface finish. These can also help determine any improper assembly, missing components, or defective products.
What is Shape Measurement?
Unlike 2D measurements involved in laser profiling, shape measurement determines the three-dimensional geometry of a particular part or component. It involves capturing contours, general dimensions, and the overall form of an object, which might be required for subsequent analysis across numerous industries and applications.
This includes design, quality control, manufacturing, and analysis. It also encompasses more than mere surface profile measurements by including all other spatial dimensions.
Shape Measurement Sensors
Shape measurements involve capturing the part or components’ overall 3D geometry, and these sensors often include CMMs for high-precision three-dimensional measurements or 3D scanning technologies that use laser scanners, structured light scanners, or photogrammetry to capture the entire 3D shape.
Shape Measurement Applications
Just like profile measurement, shape measurement is also an important part of quality assurance, as it ensures that products meet strict specifications and quality standards. Shape measurement also ensures that designs are accurately translated into physical objects, but also vice-versa, given the rise of 3D scanners that can collect and process data.
As such, shape measurements are also suited for reverse engineering applications, allowing users to capture the shape of a particular object for reproduction or digital analysis. Many industries are now integrating shape measurement sensors into their profile and shape measurement systems for real-time quality control in various processes.
Curious about our pricing?
Click here to find out more.
Optimizing Profile Measurement with Laser Snapshot Sensors
KEYENCE's profile and shape measurement solutions offer premier laser snapshot sensors for profile measurement. With high-precision, non-contact techniques, these solutions cater to a diverse array of industries.
KEYENCE laser snapshot sensors like the LJ-S8000 Series capture entire profiles in a single snapshot, making them ideal for high-speed production environments. By utilizing laser light, they ensure accurate readings, even for complex surfaces, without physical contact to avoid interference during measurement. They are particularly effective for detecting surface deformations or defects, ensuring that products meet strict quality control requirements.
Non-Contact 3D Shape Measurement Using Laser Snapshot Technology
Conventional measurement methods often require physical contact with the object, which can damage components. However, KEYENCE laser snapshot sensors for shape measurement excel at non-contact 3D profile and shape measurement. This process is suitable for objects with intricate shapes and geometries because it captures minute details with high precision. This principle applies whether it’s for automotive parts, electronics, or aerospace components, making it incredibly reliable and a well-rounded technology.
Laser Snapshot Sensors for High-Precision Shape Inspection
Laser snapshot sensors as mentioned previously are designed for high-precision shape inspection. This feature makes them indispensable for industries where accuracy is a key requirement. They can capture fine details in complex shapes and ensure that all required specifications are met. With 3D profile and shape measurement capabilities, these laser snapshot sensors for shape measurement provide precise data for evaluating surface variations, edges, and contours, minimizing defects in production.
Best Practices for Utilizing LJ-S8000 Series Sensors for Complex Profile and Shape Measurement
To optimize the use of LJ-S8000 Series sensors for complex laser snapshot sensors for profile measurement and shape measurement, it’s important that you properly align the sensor, calibrate, and monitor the environment as well. Utilizing these measurement sensors in high-speed production lines for real-time monitoring allows manufacturers to detect and correct issues instantly. This not only ensures that products meet high standards but also minimizes downtime and waste.
Are you considering high-precision shape inspection for your production line? Contact us today to learn more about how KEYENCE's laser snapshot sensors can help improve your quality control processes! Stop settling for less-than-perfect results and achieve the highest level of accuracy with KEYENCE's LJ-S8000 Series.
Are you looking to improve your quality control processes and ensure the accuracy of your products? Look no further than KEYENCE’s line of shape measurement sensors.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Related Downloads
![Key Technology and Application [Profile measurement]](/img/asset/AS_108927_L.jpg)
Conventionally, profile measurement and 3D measurement have been difficult to perform inline. This guide uses practical examples to explain how accurate, high-definition measurement and inspection can be easily achieved with the latest laser profilers.
![Measurement Application Guide [Profile Measurement]](/img/asset/AS_47103_L.jpg)
Offering a wealth of tips on profile measurement
Applications
Dimension Measurement
- Thickness and Width Measurement
- Step Height Measurement
- Inner and Outer Diameter Measurement
- Measuring Angles
- Meandering/Edge Measurement
Displacement Measurement
- Positioning and Stroke Length Measurement
- Vibration and Runout Measurement
- Deflection Measurement
- Measuring Eccentricity