Measurement Sensors
Dimension Measurement
Displacement Measurement
Positioning and Stroke Length Measurement
Real-time feedback for position or stroke is important for both process control and process improvement. The target's speed, distance, and accessibility will all impact which type of sensor best suits your needs. Take a look at the typical approaches for position measurement below, or feel free to request a consultation with a local measurement expert.
Choose Case of Positioning and Stroke Length Measurement
What is Position Measurement?
Position measurement refers to the process of determining the precise location of a particular object in space; it involves determining the object's coordinates in 1D, 2D, or even 3D environment and space concerning a relative point or line.
Position measurement is often used to measure the position of rotating or linearly moving parts in various encoders that make machinery, robotics, and precision instruments possible.
Why is Position Critical in Manufacturing?
The importance of position measuring depends on the application and industry. In manufacturing, position measurement ensures that parts are manufactured per design specifications, adhering to the correct and repeatable measurements, which is also essential for quality and functionality. It's also vital for precise positioning and component alignment in assembly lines.
Additionally, positioning is used in nearly every aspect of manufacturing imaginable. For example, consistent positioning of both tools and workpiece materials is crucial in maintaining part and component quality, as well as eliminating misalignments, defects, inconsistencies, and potential quality issues.
How to Measure Positioning
Positioning measurement involves determining the exact location of an object or its point in space, which is crucial in many different fields, including manufacturing, robotics, surveying, and navigation. Due to its widespread use, most traditional systems still rely on CMMs and probes to determine the X, Y, and Z coordinates for a point on the surface of the object. Non-contact methods, however, demand a different approach.
This saw the introduction of optical tracking systems comprised of cameras and optical sensors that would track and position objects in real-time. Alternatively, the positioning measurements are also done via laser trackers and distance meters, with the former using reflected light to measure distance and, thus, the position of an object based on its reflection.
Laser displacement is a preferable method for large-scale manufacturing applications, including aerospace and automotive sectors.
Find the best measurement method and the right equipment to measure "Positioning."
Position Control of Trim Masher Roll
Using thrubeam sensors, roller position can be accurately measured at high line speeds.
Building Material Board Positioning
Target positioning is used to ensure the next process is performed accurately. Laser profilers provide stable position feedback anywhere in the measurement range, regardless of target material, color, or size.
Tool Positioning
Robot teaching is used to ensure tools are set in the specified position. The 2D Telecentric Measurement System enables precise position feedback for end tools and other axial targets.
Wafer Notch Positioning and Dimensional Measurement
Angled mirrors can be used for measurement where installation space is limited. This setup enables position detection of tangent circle coordinates or intersection point coordinates as well as simultaneous shape and dimension verification for wafer notches.
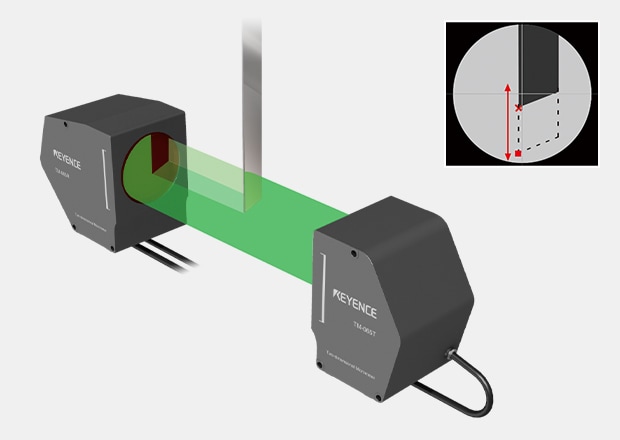
Position and Placement Measurement With a Thrubeam-Type Sensor
The edge positions of a moving target passing between the sensors are measured.
Even transparent targets can be measured stably by changing the detection threshold values of the target.
Position and Placement Measurement With a Reflectance-Type Sensor (1D Displacement Sensor)
The sensor reflects light off of the edge of the target to measure the distance from it to the target.
- Long measurement ranges and standoffs are available with select heads.
- Sensor heads with a small form factor can be used in areas with little available space.
How to Measure Stroke Length
"Stroke" is the total distance a press machine moves. In other words, the distance between its top position to its bottom position. Tracking these positions ensures that parts are pressed/stamped correctly. If a press doesn't complete its expected stroke, it could be a sign of wear on the machine or that debris/additional parts are present. If these issues aren't caught early, they could result in bad parts or - in the worst case - a broken machine.
Find the best measurement method and the right equipment to measure "Stroke."
Press Fit Failure Detection
Check for press fit failure with contact displacement sensors.
Stroke Measurement From the Side With a Thrubeam-Type Sensor
The stroke amount is measured by finding the position of the specified point using the image obtained using the 2D optical projection method.
Stroke amounts can be measured correctly with the position correction function even if the target shifts to the left or right.
Interested in accurately measuring stroke for your applications? Look no further than KEYENCE!
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Related Downloads
![Measurement Application Guide [Position Control]](/img/asset/AS_55848_L.jpg)
Offering a wealth of tips on positioning and position control
Applications
Dimension Measurement
- Thickness and Width Measurement
- Step Height Measurement
- Inner and Outer Diameter Measurement
- Measuring Angles
- Meandering/Edge Measurement
Displacement Measurement
- Positioning and Stroke Length Measurement
- Vibration and Runout Measurement
- Deflection Measurement
- Measuring Eccentricity