Inkjet printer types
On-demand type
With this method, only the amount of ink particles necessary for printing are discharged.
The ink nozzles are arranged vertically within the printer. Ink particles are instantaneously discharged from the nozzle and are sprayed on the target. Piezo, thermal, and valve are the methods used to apply pressure to the ink particles and discharge them.
Piezoelectric type (office/industrial)
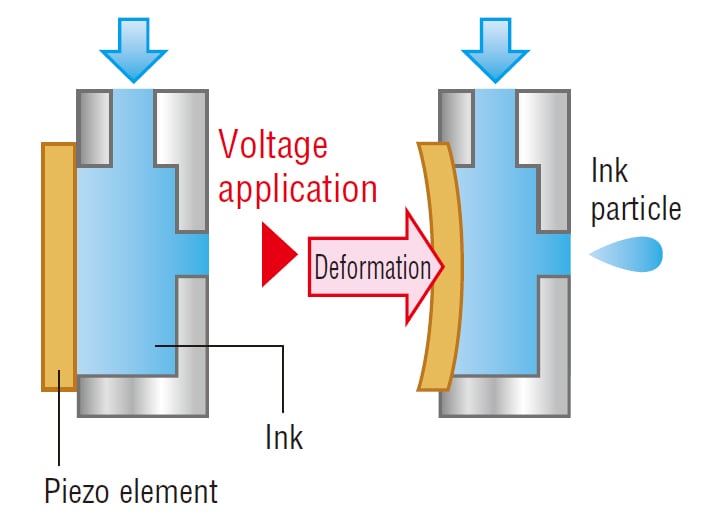
In this method, a piezoelectric (piezo) element, whose volume is deformed when voltage is applied, is used to discharge ink particles. This element is attached to the component that is filled with ink. Then, the volume deformations are used to apply pressure to the ink, which discharges ink particles from the nozzle.
| Advantages |
|
|---|---|
| Disadvantages |
|
Thermal (valve) type (office/industrial)

In this method, a heating element is used to apply heat to the ink, which causes bubbles to form and discharge ink particles. The heating element is attached to the component that is filled with ink. Applying heat to the ink causes a bubble to form, which discharges ink particles from the nozzle.
| Advantages |
|
|---|---|
| Disadvantages |
|
Valve type (industrial)

In this method, a solenoid is used to open and close the nozzle cover, which discharges ink particles.
By opening and closing the valve, the pressurized ink is discharged from the nozzle.
| Advantages |
|
|---|---|
| Disadvantages |
|
Continuous type

In this method, ink particles are continuously discharged from the nozzle. The ink particles are charge with electrostatic, and deflecting electrodes are used to deflect the ink particles so that they are spray on the printing surface.
Ink particles that are not deflected are collected, returned to the ink tank, and reused. Even when printing is not being performed, ink is continuously discharged at all times, which is why they are called continuous-type printers. This is the most commonly used method among continuous inkjet printers.
| Advantages |
|
|---|---|
| Disadvantages |
* These printers are not suited for office use. |

![Learn the Basics of Continuous Inkjet Printers [CIJ Central]](/Images/ss_products_inkjet_header_title_1785688.gif)

![Inkjet Printer Tech Guide [Basic Knowledge Edition]](/img/asset/AS_114378_L.jpg)