CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine)
Comparing 3D Scanners: Handheld vs Desktop and Other Options
In recent years, 3D scanning technology has revolutionized industries ranging from manufacturing and healthcare to art restoration and gaming. Among the variety of options available, handheld 3D scanners have garnered attention for both their versatility and ease of use. However, choosing the right scanner depends on your specific needs, as different types of 3D scanners offer distinct advantages and limitations. Let’s dive into comparing 3D scanners, focusing on handheld 3D scanners, desktop scanners, photogrammetry, and LiDAR.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

What Makes Handheld 3D Scanners Unique?
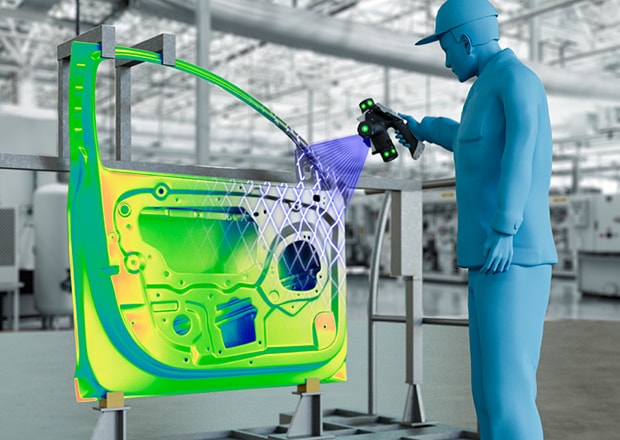
Handheld 3D scanners, like the KEYENCE WM-6000, are portable devices that allow users to capture 3D data of objects by moving the scanner around the subject. This flexibility makes them ideal for scanning objects of varying sizes and in difficult-to-reach places.
Advantages of Handheld 3D Scanners:
- 1. Portability: Lightweight and compact, these scanners can be used just about anywhere, making them ideal for applications such as scanning vehicles or heavy/hard to move objects
- 2. Versatility: Handheld scanners work well on objects ranging from small tools to semi-trucks
- 3. Ease of Use: Intuitive interfaces and real-time feedback help users ensure complete scans
- 4. Speed: High-end models can capture millions of points per second, making the scanning process efficient
Limitations of Handheld 3D Scanners:
- Stability Issues: Scanning requires a steady hand to ensure precision
- Resolution: While high-end models offer competitive accuracy, they may not match the precision of specialized desktop scanners for intricate details
- Learning Curve: New users may need some time to master smooth scanning motions
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Handheld vs Desktop 3D Scanners

When comparing handheld 3D scanners to desktop 3D scanners, the primary trade-offs involve portability, precision, and the types of projects each scanner handles best.
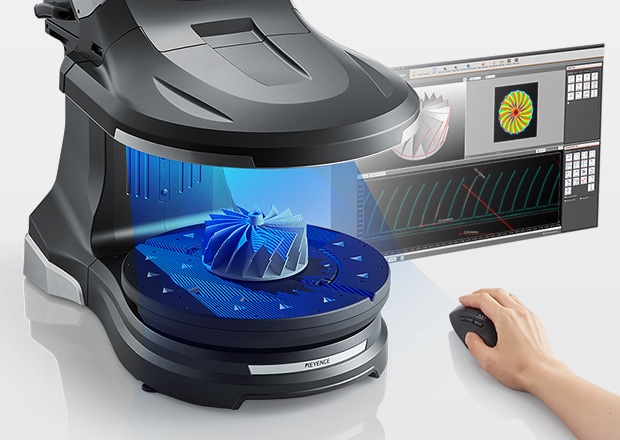
Desktop 3D Scanners, like the KEYENCE VL Series, are stationary devices designed for scanning smaller objects with high precision. The KEYENCE VL, for example, can measure parts up to 3ft, while the KEYENCE’s Handheld Scanner, the WM-6000, can measure parts up to 80ft. Desktop scanners typically use structured light or laser technology and often come with automated turntables to facilitate capturing the entire object.
Advantages of Desktop 3D Scanners:
- 1. High Accuracy: Ideal for capturing fine details, such as small engravings or intricate textures
- 2. Consistency: Scanning on a fixed platform eliminates the variability introduced by hand movements
- 3. Ease of Automation: Features like turntables reduce manual effort and improve efficiency for repetitive tasks
Limitations of Desktop 3D Scanners:
- Limited Portability: These scanners are confined to a controlled environment, such as a workshop or studio
- Size Restrictions: Desktop scanners are unsuitable for scanning large objects or environments over 3ft
- Cost: High-precision models can be expensive, particularly for occasional use
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog

Handheld vs Desktop 3D Scanners – Key Comparisons:
- Application Flexibility: Handheld scanners are better for large objects while desktop scanners excel in scanning smaller, more detailed items
- Environment: Handheld scanners work well outdoors or in dynamic settings, like a shop floor environment, while desktop scanners require stable, controlled conditions
- Learning Curve: Desktop scanners tend to be easier for beginners due to their automated features
Comparing 3D Scanners: Photogrammetry and LiDAR
Beyond handheld and desktop scanners, other technologies like photogrammetry and LiDAR offer unique benefits.
Photogrammetry:
Photogrammetry involves taking multiple photographs of an object or scene from different angles and using software to stitch them into a 3D model.
- Pros:
-
- Cost-Effective: Requires only a camera and software, making it budget-friendly
- Scalability: Works for objects as small as coins and as large as landscapes
- Detail: High-resolution cameras can capture textures and colors in impressive detail
- Cons:
-
- Time-Intensive: Requires significant time for capturing images and processing the data
- Environment-Dependent: Lighting conditions and reflective surfaces can compromise results
- Accuracy: May lack the precision of dedicated 3D scanners for complex shapes
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging):
LiDAR uses laser pulses to measure distances and create highly accurate 3D models. Commonly used in surveying and autonomous vehicles, LiDAR excels in capturing large-scale environments.
- Pros:
-
- Range: Ideal for scanning large areas such as buildings or landscapes
- Accuracy: Produces precise measurements over long distances
- Speed: Quickly captures vast amounts of data
- Cons:
-
- Cost: High-quality LiDAR systems are expensive and require specialized software
- Complexity: Processing and interpreting LiDAR data often demands expertise
- Not Ideal for Small Objects: LiDAR is not suitable for intricate details or objects at a close range
Choosing the Right 3D Scanning Solution
Selecting between handheld 3D scanners, desktop scanners, photogrammetry, and LiDAR depends on your specific requirements. Consider the following factors:
| Object Size and Detail | Portability Needs |
|---|---|
|
Object Size and Detail
|
Portability Needs
|
| Budget Constraints | Technical Expertise |
|
Budget Constraints
|
Technical Expertise
|
Conclusion
When comparing 3D scanners, it’s clear that no single solution fits all scenarios. Handheld 3D scanners shine in versatility, portability, and ease of use, making them ideal for professionals who need flexibility. However, the question between handheld vs desktop 3D scanners often comes down to accuracy and environment: desktop scanners dominate in precision for small objects, while handheld scanners excel in scanning larger or irregular objects in dynamic settings.
Photogrammetry and LiDAR also have their niches, with photogrammetry offering an affordable entry point and LiDAR excelling in large-scale accuracy. Ultimately, understanding your project’s requirements will help you choose the perfect 3D scanning technology.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
Let KEYENCE Help with Your 3D Scanner Search
The KEYENCE WM-6000 Handheld 3D Laser Scanner and CMM was built to be a one-stop solution for large part inspection.
Portability: The WM-6000 handheld scanner probe works in conjunction with a lightweight camera head unit to track the probe as it moves in the measurement area. This set-up allows the system to go wherever necessary, so you can scan whatever is needed. The KEYENCE VL Series is a desktop scanner that is not meant to be extremely portable, though it can be moved around occasionally if needed.
Accuracy: The KEYENCE VL Series boasts much tighter accuracy than the KEYENCE WM, as it scans over a much smaller area than the WM Series. While the VL can scan parts up to 3 ft, the WM can scan parts up to 80 ft, so the correct solution for a scanner would depend on accuracy and size needs,
Ease-of-Use: The WM-6000 and the VL-700 both have their own proprietary software that can be used to take measurements, import CAD models for a CAD overlay, or export for easy reverse engineering. Anyone can learn to become a user, and the software allows users to clean scanned data in seconds.
You can learn more about the WM-6000 here and the VL Series here.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Related Downloads

Brochure for the WM Series Wide-Area CMM. A portable setup with a wireless handheld probe that enables users measure large parts and equipment.




