Basics of lens selection
Basics of Lens Selection and the Effects
Image processing is the process of detecting changes in pixel density data through calculation. As such, stable detection requires projection of a clear image. The lens selection plays an important role in determining the performance of image processing–based inspection. This section introduces the basic knowledge required for selecting the correct lens.
Typical procedure for image processing
Image processing roughly consists of the following four steps.
-
- Capturing an image
- Release the shutter and capture an image
-
- Transferring the image data
- Transfer the image data from the camera to the controller
-
- Enhancing the image data
- Pre-process the image data to enhance the features
-
- Measurement processing:
measure flaws or dimensions on the image data - Measure and output the processed results as signals to the connected control device (PLC, etc.)
- Measurement processing:
Image processing flow chart

Many vision sensor manufacturers focus on explaining Step 3, “Processing the image data”, and emphasize the processing capability of the controller in their catalogs. Step 1, “Capturing an image”, however, is the most important piece for accurate and stable image processing. The key to making Step 1 a success is proper selection of a lens and illumination system. This basic guide details how to successfully capture an image by selecting a suitable lens.
Creating a highly focused imageApplication example: Detecting foreign objects/flaws inside of a cup
- When detecting foreign objects/flaws inside of a cup, which of the following two images is more suitable for detecting small defects over the entire inspection area?
- The image on the right
-
Because the cup is tall, it is difficult to get both the top and bottom in focus

-
Entirely focused image from the top to the bottom of the cup

It will be difficult to consistently detect the defects in the image on the left, even if a high-performance controller is used. With the right combination of knowledge, it will be easy to create a highly focused image like the image on the right.
POINT
Clear images are the most important part of image processing.
The following three points are essential for high-accuracy, stable inspection.
- Capture a large image of the target
- Focus the image
- Ensure the image bright and clear
Lens basics and selection methods
Lens structure
A camera lens consists of multiple lenses, an iris diaphragm (brightness) ring and a focus ring.
The iris diaphragm and focus should be adjusted by an operator looking at the camera's monitor screen to make sure the image is “bright and clear”.
(Some lenses have fixed adjustment systems)

Iris diaphragm (brightness)ring
Focus ring
※ There are various points that need to be considered when selecting a lens, such as field of view, focal distance, focus and distortion. This guide focuses on two points important for all applications, “Selecting a lens to match the field of view” and “Focusing an image with a large depth of field”.
Focal distance and field of view of lenses
Focal distance is one lens specification. Typical lenses for factory automation have focal distances of 8 mm 0.32”/ 16 mm 0.63”/ 25 mm 0.98”/ 50 mm 1.97”. From the necessary field of view of the target and the focal distance of the lens, the WD (working distance) can be determined.

The WD and view size are determined by the focal distance and the CCD size. When NOT using a close up ring, the following proportional expression can be applied.
Working distance : View angle = Focal distance : CCD size
Example 1: When the focal distance is 16 mm 0.63” and the CCD size is 3.6 mm 0.14”, the WD should be 200 mm 7.87” to make the field of view 45 mm 1.77”.
Focusing an image with a large depth of field (range in which a lens can focus on objects)
- The shorter the focal distance, the larger the depth of field
- The longer the distance from the lens to the object, the larger the depth of field
→Close up rings and macro lenses make the depth of field smaller - The smaller the aperture, the larger the depth of field
→A small aperture and bright illumination make focusing easy


A camera is installed as shown in the illustration. A graduated tape that indicates the height is attached on a slope. In this situation, the pictures are taken to compare the apertures.

Contrast differences due to lens performance
The following images are captured with KEYENCE’s high-resolution CA-LH16 lens and standard CV-L16 lens. The difference in the image quality is caused by the lens materials and structures. Higher-contrast images can be produced by using a high-resolution lens.
| Lenses used | CA-LH16/CV-L16 |
|---|---|
| Target | Copy paper |
| Field of view | 60 mm 2.36”/ Stain size: Approx. 0.3 mm 0.01” |




Comparison between a 240,000-pixel CCD and a 2 million-pixel CCD
The following images of the same target captured with KEYENCE’s 240,000-pixel and 2 million-pixel camera and magnified with a PC. Which image shows the characters more clearly? Of course, the 2 million-pixel camera. The difference in image quality directly affects the inspection accuracy when using image processing technology. Camera selection according to the application is also important.

Conventional image (240,000 pixels),2,000,000 pixels
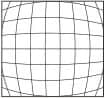
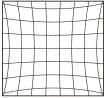
Lens distortion
What is distortion?
Distortion is the ratio of change between the center and edge areas of a captured image. Due to the aberration of the lens, the distortion is more noticeable at the edges of a captured image. There are two types of distortion: barrel distortion and pincushion distortion. The general rule is that when the absolute value of the distortion value is small, the lens offers higher accuracy. Lenses with smaller distortion should be used for dimension measurement, for example. Lenses with a long focal distance generally have smaller distortion.
Summary of lens selection and image processing basics
High-quality images are fundamental for image processing. With some is basic knowledge of lens selection:
- The suitable field of view for the target is ensured
- The entire image can be focused
- The contrast between the target and background can be enhanced with a suitable brightness
The next section will cover “illumination selection”. Along with the lens selection techniques discussed in this guide, illumination selection is an important factor for determining inspection accuracy when using image processing technology. The next guide will outline points for selecting an appropriate illumination.






![A Technical History of Image Processing Vol.1 [Camera]](/img/asset/AS_46814_L.jpg)
![The Latest Image Processing Applications [Transportation Industry]](/img/asset/AS_71759_L.jpg)

![The Latest Machine Vision Inspections [Food and Medical Industries]](/img/asset/AS_72814_L.jpg)








