Pulse Measurement Examples
Pulse measurement is used not only for measuring the speed and other properties of rotating objects but also for checking liquid flow rates and testing automotive engines. This section introduces measurement examples using pulse signals.
Basic rotation speed measurement
Because data measured by various sensors is converted to electrical pulse signals, pulse measurement is indispensable to analyzing this data. One of the most basic applications of pulse measurement is the measurement of rotation speeds. You can display the rotation speed of a gear or other rotating object by installing a sensor on it and entering the pulse signals obtained from the sensor into an instrumentation unit (data logger).

Sensors used for rotation speed measurement
Sensors called electromagnetic pickups are often used for rotation speed measurement. Various other types of sensors—including proximity sensors, eddy current displacement sensors, photoelectric sensors, and laser sensors—are also commonly used for this application. Explanations of typical sensors that can obtain pulse signals in a non-contact manner are given below.
Major sensors used for rotation speed measurement
- Electromagnetic pickup
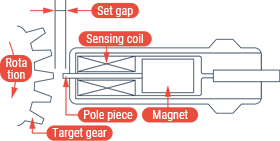
- Movement of a top land of a magnetic gear (generally an involute gear made of ferrous or similar material) closer to and farther away from the target causes the magnetic flux to change. This change generates an induced electromotive force, thereby making it possible to obtain pulse signals. This sensor’s advantages are that it does not need a power supply and it has a simple structure.
- Eddy current displacement sensor

- This is a sensor that measures changes in the distance (gap) between the metal surface and the sensor. This sensor can detect rotating pulses when used in combination with a gear having rectangular or trapezoidal teeth. This sensor’s advantage is the capability to measure a wide range of speeds—from the stopped state to high-speed rotation.
- Photoelectric sensor

- This is a sensor that emits visible, infrared, or other light and outputs signals based on the changes in the amount of light that has been reflected or has penetrated through the detected object. While electromagnetic pickups and eddy current displacement sensors can only detect metal targets, photoelectric sensors can detect most objects including those made of glass or plastic.
- Laser sensor
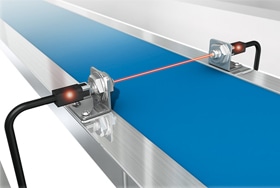
- Although the basic principle of using reflection and penetration is the same as with photoelectric sensors, this sensor is characterized by the use of a laser. This sensor also has the following advantages: easy to understand where the spotted location is, flexibility in the detecting distance, and capable of accurately measuring small objects.
Furthermore, a sensor capable of detecting on/off can output rotation speeds as pulse signals. If you want to obtain a deeper understanding of sensors, also visit the following websites.
Introductory Guide to Sensors—Sensor Basics
Click here for measurement examples of rotation speed and flow rate
Measurement of a rotation error between belt conveyors
Rotary encoders are installed on two belt conveyors and output the rotation speed as pulse signals. These pulse signals are input to an instrumentation unit (data logger) to measure the rotation speed error. The KEYENCE pulse measurement unit “NR-FV04” can receive inputs from up to four channels, thereby enabling measurement of the rotation speed of multiple belt conveyors.

Liquid flow rate measurement
Factories use liquids such as water and oil in various processes including cooling, polishing, and cutting. By installing a flow meter on the piping and obtaining pulse signals from the flow meter, you can identify the instantaneous and accumulated flow rates in the piping at a glance. With the clamp-on flow sensor “FD-Q Series,” you can measure flow rates without cutting the target piping, and this sensor’s built-in display reduces the time required for measurement.
A website that you should view before selecting a flow sensor—Flow Knowledge

Collection of PV data during engine combustion
This example uses pulse signals as triggers (measurement start signals). High-speed pulses are captured from a crank angle sensor as triggers while data is collected from a pressure sensor. The Multi-Input Data Logger “NR Series” can thoroughly follow pulses even in a high-rotation region thanks to its built-in SYNC input compatible with high-speed pulses.





