Introduction - IoT and Sensors
Industry 4.0 is the name for an innovation in the manufacturing industry. This page describes the difference from IoT and reconsiders the roles of sensors.
In line with the global trend toward IoT, there is a growing need in factories for sending important production data to host computers for centralized management. Conventionally, sensor data was transmitted through I/O wiring. Today, network connections have become mainstream because it can transmit much more sensor information in real time.
This page describes four advantages brought by networking based on Industry 4.0 that is closely related to IoT in the manufacturing industry.
What are I/O wiring and network connection?

Industry 4.0 is the name for an innovation in the manufacturing industry. This page describes the difference from IoT and reconsiders the roles of sensors.
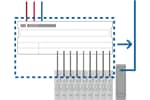
Network compatibility allows data exchange with a PLC through a single cable. The time required for conventional wiring can be greatly reduced.

Managing multiple sensors from a single point can optimize and streamline production processes through techniques such as instantaneous finding of malfunctions and autonomous local optimization.

No paper is required during start-up/regular inspections. Digital history data can be managed and retrieved easily.

Sensors can output errors and measured values in real time. Catching the signs of failures or errors allows preventive measures to be taken before the equipment or sensor breaks.