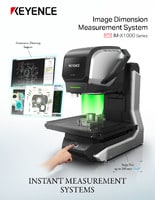
Optical Comparator (Profile Projector)
Dimensional Inspection for Injection Molding
Learn about the injection molding process, explore plastic injection molding techniques, and find the right injection molding machine for your needs. Understand the various parts of an injection mold and gain insights into the benefits and applications of injection molded products.
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a forming process for parts and components made from metal, glass, rubber, or plastic. Plastic injection molding is the most common injection molding process. It utilizes a machine that liquidizes hard plastic and then injects it into a mold for a final product.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Types of Injection Molding Machines
Hydraulic Machines
Hydraulic machines use water or oil to power the injection molding machine’s motor. The pressure from the motor can reach more than 8,000 tons for powering the mold clamps. Because of this power, this type of injection molding machine is commonly used for molding big parts or components in the automotive industry.
However, the high pressure uses a lot of energy and high temperatures. Because of these factors, hydraulic machines take longer to finish the molding process.
Electric Machines
Electric injection molding machines use servo motors to power the injection molding machine’s motor. Additionally, many of these machines use computer numerical control (CNC) software for even smarter automation. Because of the ease of using these machines, they reign popular within the injection molding industry.
Electric machines have different strengths and weaknesses compared to hydraulic machines. For instance, electric machines use toggle clamps instead of traditional clamps for holding together molds. Toggle clamps are successful with holding together smaller and more precise molds, so large automotive parts aren’t ideal for electric machines. Instead, electric machines are used for small or medium parts like medical devices.
Hybrid
Hybrid injection molding machines combine the best aspects of each machine. They use a servo motor to power the hydraulic pump to achieve intense, controlled pressure. Hybrid machines often use a two-clamp system that allows for the strength to tackle big parts coupled with the CNC software precision.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Injection Molding Step-by-Step Process
Injection Molding Process Step 1: Hopper
The first step in the injection molding process is loading granules (resin pellets) into the hopper. The hopper then feeds the granules into the cylinder.
Injection Molding Process Step 2: Cylinder
After the cylinder receives the granules from the hopper, it heats them to liquidation. Once the plastic is liquidized, it flows out of the nozzle.
Injection Molding Process Step 3: Nozzle
The liquid resin from the cylinder flows through the nozzle as it injects through the sprue (mold channel) like a syringe.
Injection Molding Process Step 4: Mold Cavity
Next in the injection molding process is the molding inside of the cavity. Since the nozzle shot the liquid resin through, the mold now cools and hardens into a shape. Once it is cooled, the finalized plastic is shot out of the mold.
Injection Molding Process Step 5: Finishing
In the last step of the injection molding process, the sprue and runner are removed for a finished part.
Injection Molding Applications
- Phone cases
- Automotive bumpers
- Cup holders
- Food/beverage containers
- Surgical preparation products
- X-ray components
Implementing Injection Molding
Injection molding is a high-quality forming process that creates plastic molds across industries. From household items to automotive infrastructure, plastic injection molding is vital to the manufacturing industry.
If you’re looking to incorporate injection molding services, consider how each type of injection molding machine (hydraulic, electric, hybrid) fits into your industry’s component sizes, efficiency, and energy use.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Quality Checks on Injection Molded Parts
For manufacturers already utilizing injection molding in their processes, they need to determine the best way to dimensionally inspect the parts they’re creating. KEYENCE's automated optical comparator utilizes vision systems to contactlessly inspect parts. It is an exceptional tool for quality checks on injection molded parts. See how it can help your manufacturing process by clicking here: KEYENCE IM-X Series.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.