Industrial Laser Marking Systems / Laser Markers
UV Laser Marking: Precision for Sensitive Materials
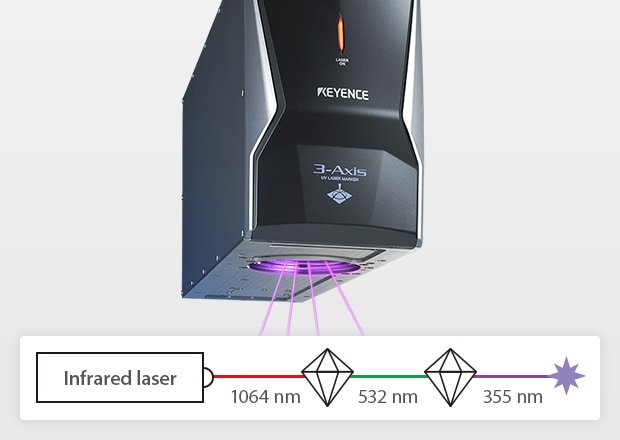
UV laser markers use ultraviolet light, typically at a 355 nm wavelength, to mark or process materials. This wavelength, about a third of the typical fiber, allows the UV laser to do things that no other laser marker can. The shorter wavelength delivers significantly higher absorption and a much smaller beam spot. This allows for high contrast and damage-free marking on metals and plastics, as well as the ability to mark smaller or more precise parts. This makes it an ideal solution for heat-sensitive materials or parts requiring precision that typical fiber lasers cannot achieve.
What is a UV Laser?
To produce a UV laser, the laser beam passes through two additional crystals that conventional fiber laser systems lack. First, By passing a standard wavelength laser (1064 nm) through a nonlinear crystal, the wavelength is reduced to 532 nm. Then, this light is further passed through another crystal, effectively reducing its wavelength to 355 nm. As a result, UV lasers are commonly called third-harmonic generation (THG) lasers because they are the third wavelength created. Marking using these lasers is called "Cold Marking," which refers to how they can perform marking and processing with minimal heat stress.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

How UV Laser Marking Works
Technology Overview and Light Properties
UV laser marking operates through precise photon absorption at the molecular level. The ultraviolet spectrum delivers photons with sufficient energy to break chemical bonds directly, creating marks without thermal processing. This non-contact marking technology eliminates physical tool wear and contamination risks.
With less divergence, the shorter wavelength offers outstanding beam quality. Unlike longer wavelengths, light at 355 nm penetrates materials differently, producing distinctive marking properties for a variety of industrial applications. At the microscopic level, the high photon energy allows for exact material change.
A modern UV laser machine utilizes sophisticated optics to maintain beam consistency. Advanced focusing systems ensure uniform energy distribution across the marking field. This precision makes industrial UV laser marking ideal for applications requiring exact specifications, including precision drilling and material bonding processes.
Differences From CO2 and Fiber Lasers
CO2 lasers operate at 10,600 nm, primarily heating materials through thermal absorption. Fiber lasers use 1064 nm wavelength, which creates heat-affected zones in many materials. These traditional systems rely on thermal processing that can damage sensitive components.
UV systems offer superior precision through cold processing techniques. The shorter wavelength enables marking on reflective surfaces where other lasers struggle. Materials that reject infrared wavelengths readily absorb UV energy, expanding application possibilities.
Processing speed varies significantly between laser types depending on material properties. UV laser marking excels on plastics and delicate components where thermal damage is a concern. Traditional lasers may process faster on thick metals, but they lack the precision required for miniature components.
Why Choose UV Laser Marking?
Manufacturers across the globe use UV laser marking due to its precision and ability to work on sensitive materials. The shorter wavelength (often 355 nm) allows UV lasers to create detailed, high-contrast marks on materials like plastics, ceramics, and glass without causing heat damage. Using a UV laser marking machine allows for minimal material alteration, which is especially important for marking items like microchips or delicate medical devices.
UV laser markers are the best option for marking materials that reflect longer wavelengths when compared to other laser technologies. They excel at creating clear, high-contrast marks on transparent or highly reflective surfaces. In contrast, other lasers, such as infrared or CO2, struggle to achieve the same level of precision without causing damage.
The precision offered by UV laser technology also ensures that barcodes, logos, and detailed product information can be clearly marked, even on the smallest components. One final reason UV lasers are often chosen is that they operate at higher speeds. Production efficiency, while maintaining the quality and durability of the markings, is easier to achieve.
Key Benefits of UV Laser Marking
Non-Contact, Damage-Free Processing
Non-contact marking technology eliminates mechanical stress and contamination during processing. No physical contact means zero tool wear and consistent marking quality over time. This method stops the production of particles that can jeopardize clean room conditions.
The molecular integrity of the substance is maintained by the cold marking process. Structural strength and corrosion resistance are preserved by the surface's unchanging characteristics. For parts that require precise material specifications, this advantage is crucial.
Processing flexibility allows marking on curved, fragile, or irregularly shaped items. The laser beam can access tight spaces where mechanical tools cannot reach. This capability enables marking on assembled products without disassembly requirements.
Permanent Marking on Heat-Sensitive Materials
Heat-sensitive polymers, electronics, and medical devices require gentle processing techniques to ensure their integrity. UV laser marking machine systems deliver energy without thermal buildup that could damage components. The photolytic process creates permanent marks while preserving material properties.
Glass, ceramics, and thin films benefit from UV processing capabilities. These materials are frequently cracked or overstressed by conventional marking techniques. On sensitive materials, UV wavelengths allow for precise labeling without sacrificing structural integrity.
Surface treatments and coatings that are sensitive to temperature do not break down when exposed to UV light. The functionality and appearance of the product depend on this preservation. Industrial UV laser marking systems deliver consistent results across a wide range of material thicknesses and compositions.
KEYENCE UV Laser Markers
The UV laser markers from KEYENCE are made to be durable and adaptable for use in high-precision marking tasks. When it comes to marking medical instruments with Unique Device Identification (UDI) codes or labeling electronic components with batch numbers and traceability codes, for example, KEYENCE UV lasers are perfect for sectors where strict regulations are in place. Manufacturers use these machines for scalability and ease of operation, and they can be installed in a flexible way into current production lines.
The MD-U Series 3-Axis UV laser marker utilizes a 355 nm wavelength for cold-marking technology, allowing for precise marking on 3D shapes and large fields of view (up to 330 mm × 330 mm). Their three-axis control maintains a consistent focal distance, ensuring distortion-free markings across various surface heights and geometries. A built-in camera enhances functionality by enabling autofocus, 2D code reading, and live marking verification, streamlining the marking process for complex shapes and ensuring accuracy.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.
UV Laser Marking vs. UV Laser Engraving
The distinction between UV laser marking and engraving lies in the depth and technique. UV laser marking typically alters the surface layer of a material to create high-contrast marks, but it does not remove material. Ideal for applications where permanent, non-invasive marking is needed, marking is useful where surface integrity must remain intact.
On the other hand, UV laser engraving uses a deeper process, physically removing material from the surface to create more tactile designs. Laser engraving large surfaces or designs can be more difficult with UV lasers, due to the lower heat reliance. However, the high energy density and small beam spot make the UV laser a good choice for precision cutting for thin materials that can't sustain heat damage. While both techniques offer precision, UV laser etching machines are best for products that need to retain their surface properties while still benefiting from long-lasting, high-contrast markings.
UV Laser Marking Applications
As mentioned, UV lasers feature a highly absorptive wavelength of 355 nm. This is dramatically shorter than general laser marking and processing systems, which allows many materials to absorb it at a much higher rate. The shorter wavelength also allows a UV laser to perform "cold marking." This is characterized by photolytic processing of the material bonds to create contrast or remove material.
General lasers use a thermal process of vibrating the bonds of material via heating to the point that they break. This often leads to a heat-affected zone (HAZ), which is a zone surrounding the mark where material properties are changed due to heat exposure. This can damage products or create more scrap.
UV lasers remove the risk of this heat-affected zone as marks stay at a higher surface level while still creating permanency. A UV laser is ideal for almost any plastic, resin, glass, rubber, or ceramic needs, as well as any metal marking or processing application where the effects of laser marking on the materials' surface finish may be a concern.
UV Marking in Critical Industries
Regulatory Compliance and Serialization
Medical device manufacturers must meet stringent traceability requirements to ensure patient safety. UV laser marking creates permanent identification codes that withstand sterilization cycles. The marks remain legible through multiple cleaning and disinfection processes required in healthcare settings.
Pharmaceutical packaging requires tamper-evident marking with precise readability standards. UV systems create high-contrast codes on various packaging materials without compromising barrier properties. This capability ensures product integrity while meeting regulatory demands.
Accurate component identification is necessary for quality control and recalls in electronics manufacturing. Small parts can be marked using UV laser machine technology without altering their electrical characteristics. The non-thermal method is perfect for automotive applications where dependability is crucial to protect delicate circuits and connection integrity.
In-Vehicle Plastic Parts

Polyamide (PA)
Earbuds

PVC
LED Lights

ABS
Multicolor Automotive Relays

PBT
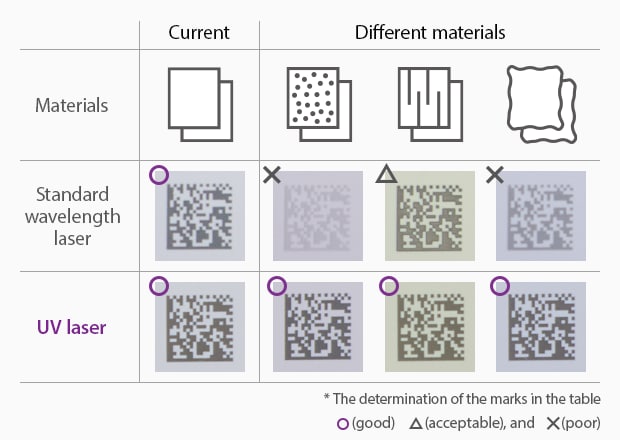
Highly Robust Against Material Inconsistencies
UV lasers eliminate the need for tricky readjustment of laser marking parameters to counteract contrast decreases due to material changes, inconsistent surface conditions of molded parts, and different resin lots. With high contrast, this robustness provides the characteristics, including resistance against ambient light, that enable marking operation with fewer failures.
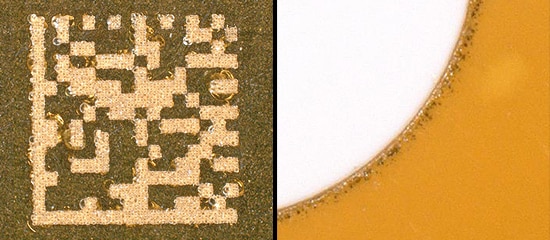
UV Laser High-Contrast Marking Application
The FDA requires all but Class I medical devices to contain traceability codes that machines and people can read. The "cold marking" process allows medical manufacturers to mark anything, from PE medication bottles to implantable devices, with the confidence those marks will withstand stringent sterilization cycles.
Absorption Rate for Plastics
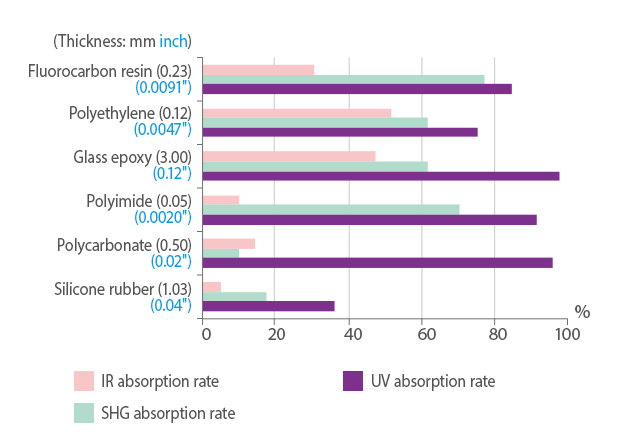
Absorption rates for various resin materials
* The values are for reference only and do not account for surface reflectivity
Absorption Rate for Metals

Light absorption rate for metal
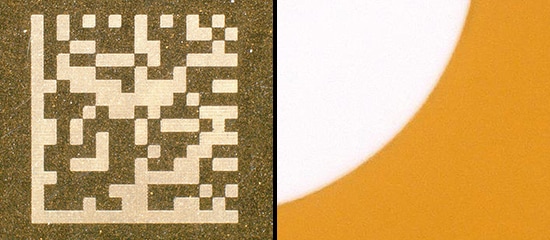
UV Laser Marking Feature: Damage-Free Marking & Processing
Why is a UV laser marking machine the superior choice in these types of applications? The main reason it was developed is that the absorption rate is incredibly high for a variety of materials. This allows marking and processing to be performed with minimal heat stress. It also reduces surface damage, allowing for corrosion-resistant marking. These attributes protect the materials or components from issues during the marking and manufacturing process. This is true even for highly reflective materials like gold, silver, and copper and sensitive materials like glass, rubber, ceramic, and plastic.
Perform Both Marking and Processing Without Thermal Damage
Standard Wavelength
Marking / Cutting
MD-U
Marking / Cutting
Thermal Processing
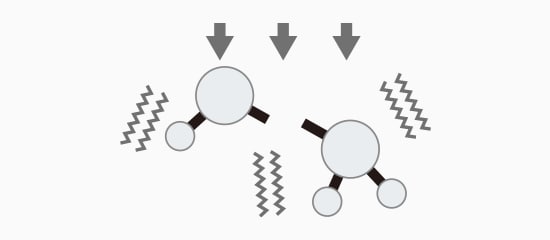
Bonds are destroyed using heat to vibrate the molecules.
Photolytic Degradation Processing
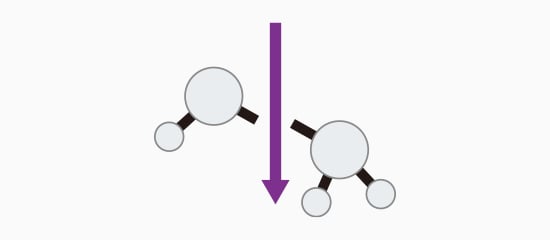
Bonds are broken with light, resulting in less heat.
Conventional
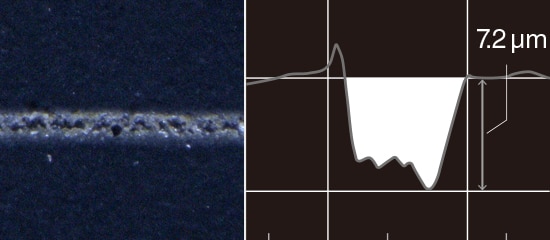
UV Laser
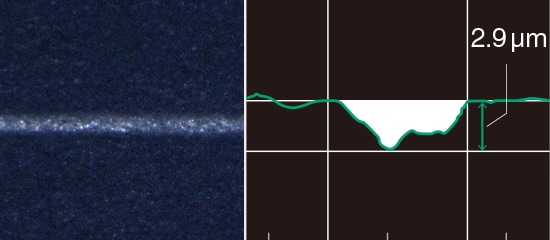
Marking with reduced amount of engraving.
UV Laser Damage-Free Marking Application: Electronic Parts
Electronic parts are becoming smaller, and their sealing resins are becoming thinner. Typical laser markers risk transmitting energy through sealing resins and damaging the internal components. However, UV laser markers have an incredibly high material absorption rate and can mark sealing resins without reaching down to the internal components and risking damage. Since a UV laser marking machine can mark sealing resins, manufacturers can add more identification or traceability marks to electronic part surfaces. Customers and manufacturers get quicker recalls and more up-to-date product information.
UV Laser Damage-Free Marking Application: Quartz Glass
Quartz glass is used for windows or screens and is notable for being difficult to mark. It's sensitive to cracks yet heat resistant, requiring a gentle marking method. The UV laser uses its high absorption and power-dense beam spot to mark slowly and produce clean, visible marks. The UV laser marker beam is strong enough to conquer the heat resistance yet delicate enough not to crack the quartz glass.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Product Introduction
3-Axis UV Laser Marker MD-U Series
The 3-Axis UV laser markers use a UV wavelength of 355 nm to mark or process parts with cold-marking technology. These markers have three different axes to control the laser beam, designed for uniform marking over large fields of view or 3D shape parts. UV laser marker systems incorporate groundbreaking technology that is revolutionizing the way we mark and engrave objects. Additionally, a 3-Axis laser marker allows complete control of the focal distance to keep the laser in focus through different height parts or difficult geometries.
Uniform Marking
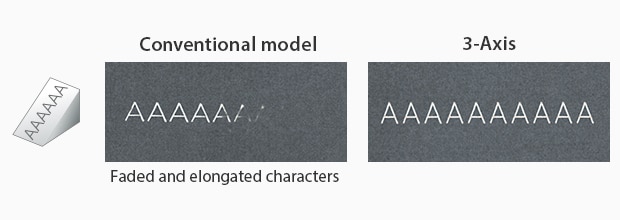
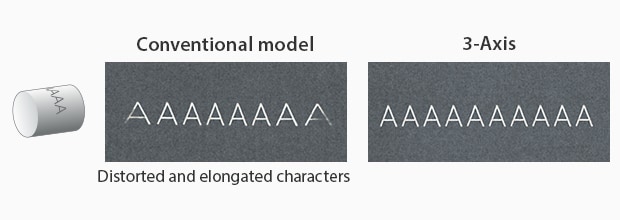
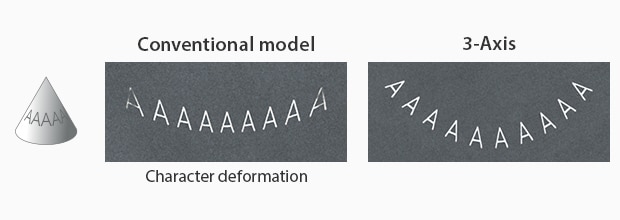
The 3-axis control adjusts the focal point throughout the UV laser marking process to maintain distortion-free marking over the entire field of view by constantly adjusting the point at which the laser comes into focus. Because of the adjusting focal point, the beam will remain in focus throughout a much larger field of view (330 mm x330 mm), where conventional laser markers can't.
3D Shape Marking
The 3-axis control also addresses one of the most common concerns within laser marking and processing: 3-dimensional shapes. Where conventional systems are constrained to working in a single plane, KEYENCE systems are able to variably adjust their focal points to stay in focus on multiple-step heights, cylinders, inclines, cones, spheres, or even map to a CAD image of on-standard shaped products.
Multi-function built-in camera
A built-in camera in the MD-U UV laser marker enables autofocus, 2D code reading, marking confirmation, and a built-in finder view to map your marking program on a live image of the product under the laser.
Conventional
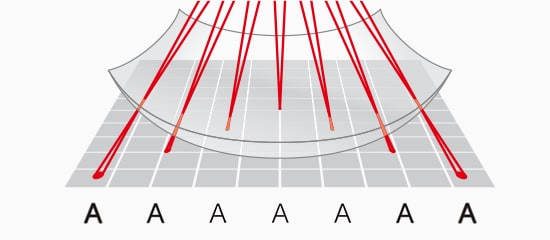
3-Axis
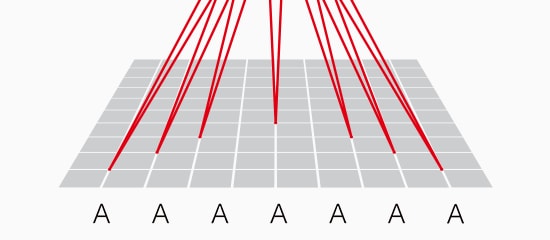
Steps
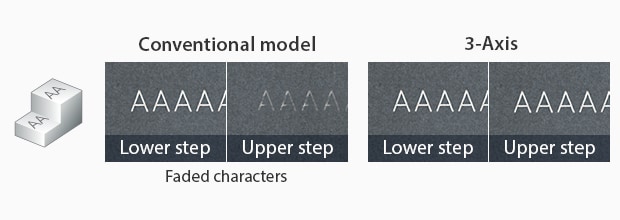
Inclined Surface
Cylinder
Circular Cone
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Small Beam Spot and High Beam Quality
The wavelength greatly impacts the spot diameter of a laser. Since UV lasers are 1/3 the standard Fiber wavelength, the spot size is narrowed accordingly. This opens the possibility of marking where there is extremely limited space and where marking was not an option before. There is also a continually rising demand for manufacturers to reduce the component size and increase functionality, so the ability of the UV laser to mark the finished product and individual components is very unique.
Issue
An increase in the number of markings required due to traceability improvement.
Solution
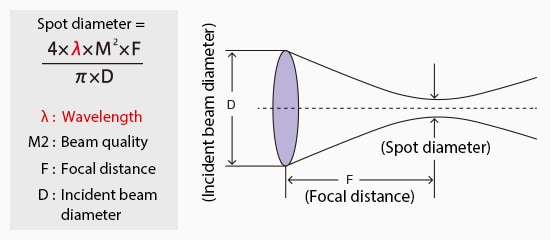
Laser marker spot diameter
Clear marking when space is limited.
IP64 Rating
The MD-U Series uses a proprietary sealing method to securely protect optical components. This ensures that these components are not affected by factors such as dirt, dust, and water. This also provides environmentally resistant performance, which allows for stable operation in even the harshest environments. The MD-U Series has an enclosure rating equivalent to that of the fanless marking head of the MD-F. This is not the case for other UV laser marking systems.
Get Started with KEYENCE UV Laser Technology
Getting started with a KEYENCE UV laser etching machine is simple, thanks to our advanced technology and support. Whether you're looking to mark intricate details on medical devices or ensure long-lasting product codes on electronic components, KEYENCE has a UV laser solution.
Contact us today to explore how our cutting-edge laser technology can elevate your marking capabilities.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
FAQs
Why Are UV Lasers Preferred for Marking Medical Devices?
They produce fine, sterile, and precise marks without damaging the surface or compromising hygiene. UV wavelengths create permanent identification codes that survive sterilization cycles.
Is UV Laser Marking Suitable for Dark Plastics?
Yes, UV lasers work well on dark and transparent plastics due to their short wavelength and high absorption. The 355 nm wavelength provides excellent contrast on various plastic colors.
How Long Do UV Laser Markers Typically Last?
Conventional UV systems offer about 10,000 hours of marking with minimal maintenance when used in clean environments. However, KEYENCE UV laser markers are rated for 10 times the life span as conventional UV lasers.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!




![UV Laser Marker Application Guide [High Contrast Marking]](/img/asset/AS_95184_L.jpg)
![UV Laser Marker Application Guide [High-Contrast, Damage-Free Marking]](/img/asset/AS_96215_L.jpg)

