Static Eliminators / Ionizers
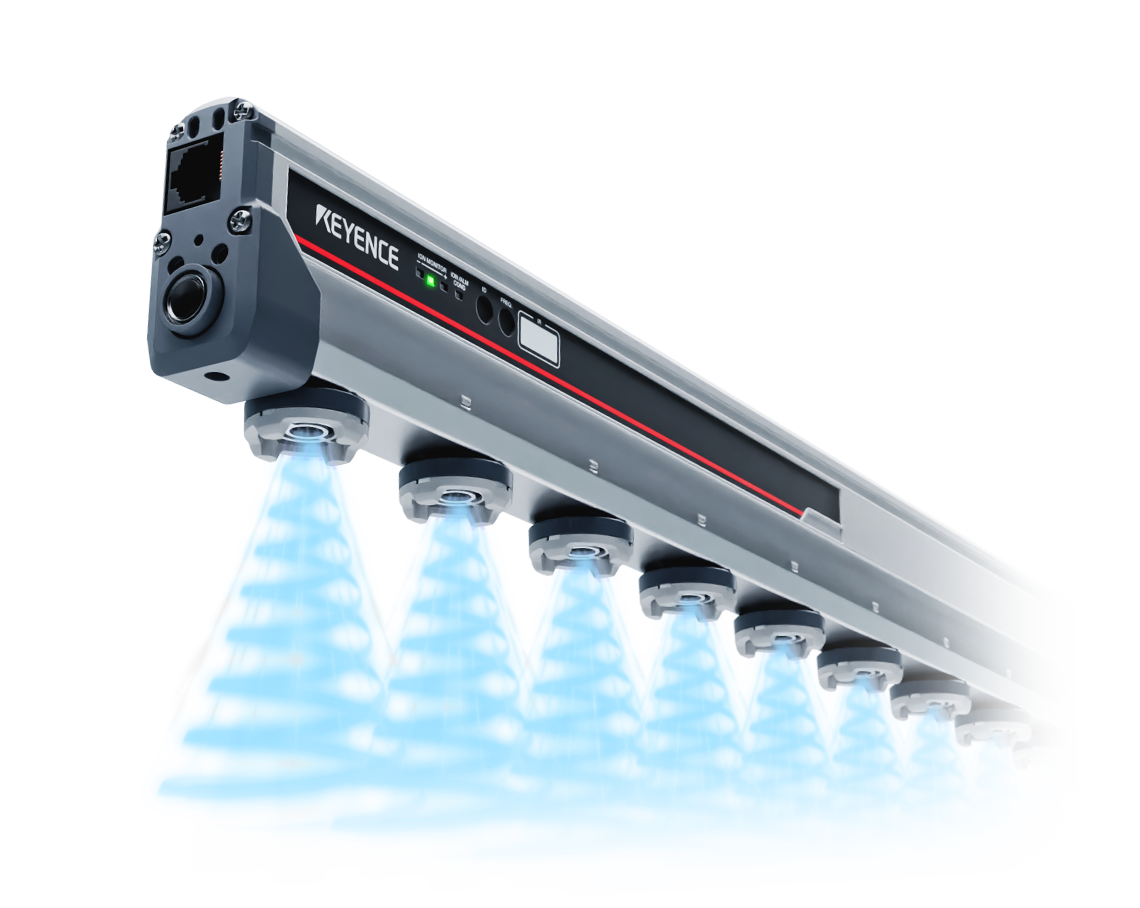

A static eliminator that eliminates static electricity in a variety of environments, from the entire room to precise locations.
The product lineup includes a stick type with a small flow rate and sufficient static elimination performance;
a fan type that does not require an air supply; a point type that fully eliminates static electricity in necessary parts;
and an air gun type that can be used anytime and anywhere, etc.
Product Lineup : Bar Type

The High-Accuracy High-Speed Sensing Ionizer SJ-Q Series provides 10 times the static elimination performance of conventional models (ion balance: ±3 V, static elimination speed: 0.1 s). This greatly reduces conventional static eliminator problems: risks as well as time and effort related to electrode probe cleaning and wear. This product provides completely maintenance-free reliable static elimination. Conventional electrode probes must be replaced every 1 to 2 years, but with this product they do not need to be replaced for 10 years. The electrode probe cleaning that had to be performed every 2 to 4 weeks also only needs to be performed once a year. The result is a major decrease in ionizer running costs. The world’s first Inside Supersonic structure will change the way you think about static electricity countermeasures.
Features
Maintenance-Free
No Electrode Probe Replacement Required for 10 Years
Accurate static elimination is provided even with probe wear. The Hi-Power I.C.C. system monitors the ion generation status at all times. The applied voltage is automatically increased as the probe wears down.
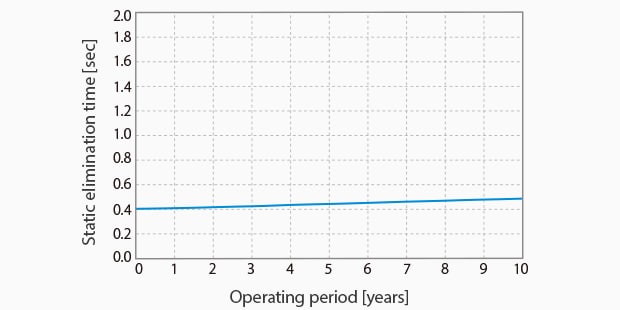
Operating period and static elimination time
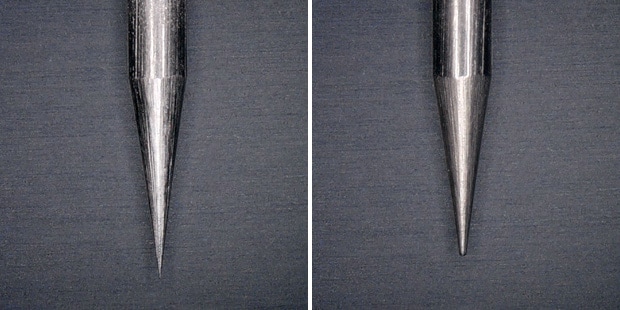
Left: New electrode probe
Right: Worn electrode probe
No Electrode Probe Cleaning Required for 1 Year*
Probes are protected from dust and other debris to provide accurate static elimination for as long as possible. Supersonic air is sprayed coaxially onto the electrode probe, enveloping it and repelling dirt from outside air.
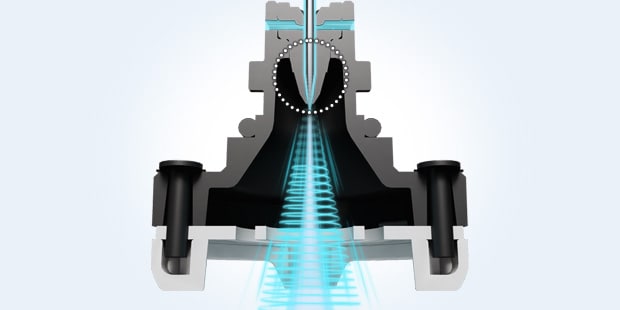
Inside Supersonic structure
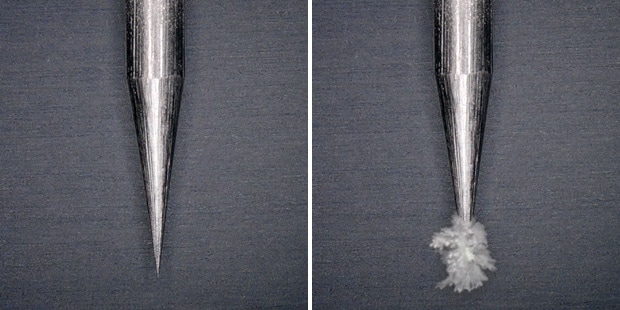
Left: New electrode probe
Right: Dirty electrode probe
Reduced Operating Costs Over 10 Years of Use
* Annual electricity bill calculated at 0.18 $/kWh. Comparison of simulations when supplying 0.5 MPa 72.52 PSI CDA to the SJ-Q108 for 10 years and 0.5 MPa 72.52 PSI CDA to the conventional SJ-H108 for 10 years.
Example of Factory Air Costs for Ionizers
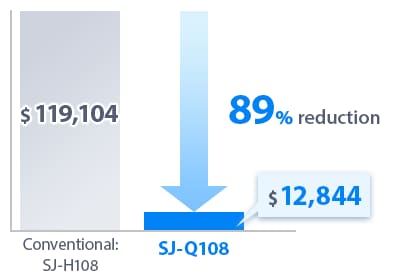
Example of Electrode Probe Costs

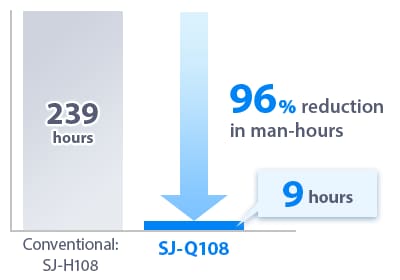
Example of Labor Hours Required for Cleaning Electrode Probes

The Energy-Saving High-Speed Sensing Ionizer SJ-E Series saves energy while still providing high-speed static elimination. The supersonic air flow and structural optimization of electrode positions successfully reduce air consumption by 60% compared to conventional models. The result is static elimination with minimal running costs, a necessity amid rising electricity costs and the trend toward SDGs. Furthermore, the utilized supersonic structure reduces the adherence of foreign particles to static elimination probe tips, minimizing the need for maintenance even though a low volume of air is used.
Features

The Three Technologies That Support Our Ability to Provide Optimum Static Elimination with the Lowest Air Volume in the World
By using the first supersonic structure ever developed in the history of ionizers, KEYENCE has increased the speed of ions past the speed of sound, which makes the fastest static elimination in the world possible with an extremely low air volume.

Optimum Static Elimination & Energy Saving
We have used de Laval nozzles, which are used in supersonic jet engine technology, in the electrode probes to realize our supersonic structure. The air speed exceeds the speed of sound, which enabled us to rapidly improve the speed at which ions attach to the target. In addition, the shape of the electrode probes, which makes use of fluid mechanics, pulls in the surrounding air to increase the air volume. These two technologies are what enable static elimination at high speeds and over a wide range with the lowest air volume in the world.

The Air-Free High Speed Sensing Ionizer SJ-H Series can provide high static elimination performance even without utilizing air. This makes it the optimal device for situations where static elimination is required but no air can be used. To meet a variety of static elimination needs, the lineup includes a model with clean pack specifications and a silicone probe model. This ionizer can be used in a wide variety of applications.
Features
High-Speed Static Elimination without Air
I.R.G. design for optimal ion flow
In conventional models, the ground plate is externally mounted. KEYENCE's SJ-H Series is the first to use I.R.G. (Insert Ring Ground) technology in which the ground plate is housed internally. By directing the generated ions to the target rather than the ground plate, the total number of ions that reach the target increases. This allows for high-speed static elimination that is five times faster than conventional models.

High Usability
The SJ-H Series includes a self-diagnosis function that monitors the ion generation level. With the bar LED and alarm outputs, the ionizer alerts you when maintenance is required.

Product Lineup : Blower / Fan Type

The SJ-F700 Series Multi-Sensor Ionizer offers complete automation of periodic maintenance - an essential task with any static eliminator. Both probe cleaning and maintenance are done automatically by the unit, which eliminates the need to check static elimination performance. Offering completely maintenance-free operation while ensuring continued best-in-class static elimination (with an ion balance of +/-1V, elimination speed of 0.5 sec, and a static elimination area of 3m (9.8')), the SJ-F700 makes it easier than ever to solve static problems. Make use of maintenance-free static elimination with the SJ-F700 static eliminating blower for ESD (electrostatic discharge) and foreign object adhesion.
Features
Say goodbye to probe cleaning and replacement
Never worry about having to clean or replace electrode probes again.
In addition to an auto-clean function that protects probe tips, the SJ-F700 Series also includes a multi-I.C.C. for maintenance-free operation.
- Variable DC system
- High-density brushes
- Brush cleaner

High-Performance Static Elimination
- Ion Balance +/- 1V for high-accuracy electronics applications
- High Speed Static Elimination: Remove static in as fast as 0.5sec
- Wide area elimination up to 3m

Static elimination example

SJ-LF Series compact fan static eliminators are anti-static blowers that allow operators to “see” whether there is static and “verify” that static has been removed. The “visualizing light” and large indicator display the electrostatic level. This means that it is possible to instantly determine whether the static on the target object has been properly eliminated, making operations checks during startup easy. The compact body is one-fifth of the size of conventional small blowers, which gives the SJ-LF an array of different installation options. The main unit itself can generate airflow, so there is no need to supply air from a compressor. The SJ-LF Series is a lineup of static neutralizing blowers that embody solutions to on-site needs, alerting operators to errors and failures with alarms, including an ion level alarm.
Features
Visualizing Light: Static Electricity is Visible
Confirm if static was eliminated from any angle. Check operation without any additional sensors and easily reduce the problems caused by static electricity.
Static electricity present

Orange
Static electricity absent

Green
Smallest in Class: Fits in the Palm of Your Hand
The SJ-LF is small enough to be mounted anywhere, enabling it to be retrofit into existing equipment or installed in tight spaces where conventional static eliminators won't fit.


SJ-F2000/5000 high-speed, high-accuracy wide static elimination blowers are wide sensing ionizers that neutralize static-induced problems by removing static from the environment, including products, human bodies, and peripheral parts. The fastest-in-class static elimination performance and high-precision ion balance, together with the wide-range airflow adjustment function, support various settings for a static-free environment. Because ions are supplied at the optimal balance that matches the electrostatic charge, no cumbersome initial settings are required during implementation or maintenance, delivering even more effective static electricity elimination. SJ-F2000/5000 Series static elimination blowers offer high performance and excellent usability at a higher level. With functions that suppress wear and dirt build-up in the elimination probe, the static control system employs a structure that allows easy maintenance, and a compact body that takes little space for installation.
Features

Highest Static Elimination Speed in Its Class
Through the combination of the well-proven pulse AC method and I.C.C., the SJ-F2000/F5000 Series has achieved the best ion generation per electrode in its class.
A high-power fan and a louver structure have been incorporated to provide a wide static elimination area with the fastest speed in its class.

Low Maintenance
KEYENCE's original I.C.C. has been incorporated to reduce the degradation of static elimination speed resulting from worn or dirty probes and to achieve three times longer operation with low maintenance compared to conventional models.
Product Lineup : Spot / Nozzle Type

Features
Installable Anywhere!
Multi-Angle Static Electricity Elimination
Achieve static electricity elimination at any angle without having to change mounting positions. Never worry about not having enough space for retrofitting equipment or needing to remove static electricity at specific locations.

Easy Determination of Effectiveness!
Light-Based Static Electricity Visualization
Determine the static charge of targets with color. The ability to quickly verify whether static electricity has been removed properly at any angle makes it possible to easily check static electricity elimination effects at startup and during operation.

The high-performance SJ-M Series micro static eliminators are used as ultra-small embedded static eliminators. Spot nozzles and wide-area electrode probes are available depending on the required range of static elimination. Spot nozzles can focus on ionization and be built into a system designed to withstand high temperatures up to 80℃. The high-functionality controller indicates the static elimination status with an electrostatic monitor that shows the level of electrostatic charge of the target object, an ion level monitor that self-diagnoses and displays the ion level, and a condition monitor that displays and outputs an alarm when the static elimination effect is insufficient. In their small enclosures, the SJ-M Series micro static eliminators embody versatility that covers both spot and wide-area applications, a robustness that endures high temperatures, and best-in-its-class static elimination performance.
Features
Ultra-small Static Elimination Head Can Be Mounted Anywhere
Since the SJ-M Series provides a direct static elimination structure that directs the ion generation point at the tip of the head, it allows for high-speed and high-precision static elimination where it is needed most.

Static Elimination over Areas at Distances of 1 m or More Using a ⌀12 mm Diameter Sensing Head
Remove static electricity from an area as large as 600 × 1500 mm using just a compact head. Eliminate static from more than 1 m away in under 1 second. Use branching to remove static electricity from inside devices.
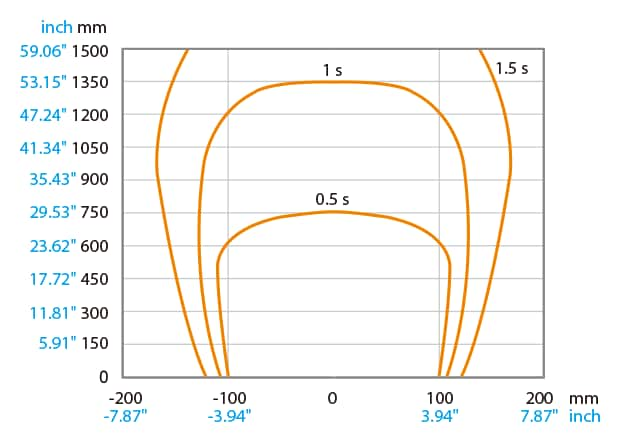
Static elimination range and time (typical) (Applied pressure of 0.5 MPa)
Product Lineup : Gun Type

Features
Impressive Dust Removal Performance 3× More Powerful
The device’s Laval nozzle structure—which is also used in jet engine technology—pushes out air at supersonic speeds. Adding ions to this ultra-high-speed air helps not only remove foreign particles but also keep particles from re-adhering.
Ultra-robust All-in-One Design
The device’s ultra-rugged body is equipped with a rubber protector capable of withstanding strong impacts, preventing breakage even when the device is dropped from 2.0 m 6.6′. The long service life and highly durable design ensure the device can be used with confidence even in frequently used sites.

A static eliminator neutralizes electrostatic charge by releasing positive and negative ions. When static-prone surfaces come into contact with these ions, their charge is balanced, preventing static buildup and reducing potential damage or interference in manufacturing processes.
Benefits of Static Eliminators / Ionizers
In warehouses that store electronic parts and films, charged ions need to be delivered quickly over a wide area to reduce static. A bar-type static eliminator can neutralize a wide area of space.
In the pulse AC method, the positive and negative voltage is applied alternately to a single electrode probe, generating ions of both polarities. In the pulse DC method, each electrode must be positive or negative. This pulse AC method performs well under all conditions as more ions are generated than in the conventional method and the ratio of positive to negative ions can be changed. By delivering ions throughout the entire room and removing the electrostatic charge from airborne particles, the ionizer can prevent them from being attracted to surfaces. Also, using a bar-type ionizer in front of the entrance to a static-free site can prevent static charge and particles from being brought in by operators.
Using a dust collector in a process that transfers electronic parts can make sheets and films flutter because of the vacuum. In addition, the air may cause small, light electronic parts to be blown away. Ionizers that do not use blowers can eliminate static charges without unwanted excess air.
Non-blower type ionizers remove static charges from delicate parts that are sensitive to dust and wind pressure without using air. For example, an airless ionizer can remove static charge from thin sheets and films without making them flutter. This allows fine parts to be neutralized without being affected by wind. The efficient delivery of ions to target objects helps the elimination of static electricity over a wide area, even without the use of supplied air. Even compact, space-saving spot types can airlessly remove the static charges.
The anti-static method of blowing off dust can generate static charge and cause dust to stick to surfaces again. Using ionizers for static elimination can also remove dust. This can neutralize products and prevent dust from re-adhering once static elimination takes place.
Ionizers that remove dust by high-pressure air purges remove dust and static electricity at the same time. Static is eliminated when dust is blown off, neutralizing the target object and preventing re-adherence. These ionizers can be attached to conveyor systems for static elimination and dust removal of products during transfer, as well as be used at entrances to cleanrooms.
Static Eliminator / Ionizer Case Studies
Automotive
Static eliminators help prevent static buildup during automotive assembly by reducing dust and dirt contamination.
Food
In food processing and packaging, static eliminators neutralize static to maintain smooth product movement and prevent contamination from static-induced dust.
Pharmaceutical
Static eliminators in pharmaceutical cleanrooms neutralize static, helping to maintain sterile environments and reduce the risk of contamination in drug production.
Electronics
Static eliminators prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) from damaging sensitive electronics during assembly and testing.
Semiconductors
Static eliminators reduce static in semiconductor production lines to produce high-quality microchips and minimize defects.
Plastics
Static eliminators neutralize static in plastic molding and prevent parts from sticking to equipment, supporting smooth handling and improved quality.
Reduce electrostatic risks with KEYENCE’s advanced static eliminators today!
Adhesion of foreign particles
How particles adhere to surfaces depends on whether the surface is conductive or non-conductive. In either case, an ionizer can be used for prevention. If the surface is plastic or rubber, or any other kind of non-conductive material, and the location of static buildup is known, particle adhesion can be prevented by localized static elimination. On the other hand, with conductive surfaces, the particles themselves can be neutralized to prevent adhesion. A bar-type static eliminator can be used for a large space where airborne particles are present to eliminate static from the entire room. In this case, removing the electrostatic charge from airborne particles can prevent them from being attracted to surfaces.
Static discharge on people
Humans constantly accumulate charge when moving. A bar-type static eliminator can be used for a large space where airborne particles are present to eliminate static from the entire room. To eliminate static from large spaces, the neutralizing ions must be carried long distances. Some ionizers can have different cycles (frequencies) to generate positive and negative ions. Lower frequencies make for a longer emission time of ions of the same polarity, which makes them repel each other and spread wider. In contrast, higher frequencies switch positive and negative ions rapidly, which causes like ions to be attracted to each other and prevents them from traveling any significant distance. The frequency should be set lower for static elimination for large spaces.
Problems in transfer processes
Problems in transfer processes can vary, including incoherent pass-over timing, friction or suction on object surfaces, chemical affinity, magnetic force, and static buildup. Among such factors, static electricity tends to be a common culprit for transfer trouble at manufacturing sites. Such problems can be solved by making the Coulomb force―be it attractive or repulsive―disappear, which specifically means to remove the static charge. For example, in case of a problem of sheets sticking to a roller, an ionizer should be aimed at the point where the sheet leaves the roller. In another example where parts from a part feeder lift up and do not flow well on the conveyor, an ionizer should be aimed at a point between the rail and parts for static elimination.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage
Electrostatic discharge can destroy electronic parts. This problem occurs when the accumulated electrostatic charge is discharged and causes a larger current than normal to flow in the circuits, generating heat that destroys the electronic part. The three key points in preventing ESD damage are: suppressing electrostatic generation, eliminating static buildup, and preventing electrostatic discharge. The specific solutions to these problems are grounding, adding conductivity, and static elimination (ionizers). Notably, ionizers can be useful when grounding is unavailable. Damage to electronic parts can also be caused by electrostatic charge (accumulated by the electronic part itself) discharging inside the electronic device. In such cases, the parts themselves must be neutralized, a task for which ionizers are effective.
Damage to electronic equipment and devices
Where static electricity is discharged, there is always electromagnetic noise. This electromagnetic noise can cause malfunctions in electronic equipment and devices. With such a malfunction, the problem is not the amount of electrostatic charge, but rather the electromagnetic noise generated when the electrostatic charge is discharged. This means that it is important to prevent electrostatic discharge and electromagnetic noise generation. Specifically, grounding and static elimination (ionizers) can be used for these problems. For example, on a can manufacturing line, charged cans can discharge static, generating electromagnetic noise that ends up stopping the system. A static eliminator (ionizer) is used to prevent such malfunctions. As static eliminators (ionizers) can eliminate static without coming into contact with products, it is easy to add them onto existing production lines.
Application and marking problems
Application and marking problems are sometimes caused by forces described in Coulomb's Law. If the material to be painted is negatively charged before the application process, it is possible that the paint, sealant, or whatever is to be applied will be repelled. This is due to Coulomb's Law. Application and marking problems can be solved by making the Coulomb force disappear. More specifically, use an ionizer to remove the static charge. An ionizer used to prevent application or marking problems can be installed so that the ionizer focuses on the intended area. A nozzle-type ionizer is suitable for installing in such narrow spaces.
KEYENCE’s SJ Series static eliminators come with a host of features that can be customized for high-performance industrial environments. The SJ-LM Series, for instance, is designed to maintain ion balance automatically, maintaining maximum efficiency without constant manual adjustments. The SJ-E Series is similar but offers low-power consumption, a design that makes it more energy-efficient for long-term operation. Regardless of the model, these devices are built for durability and are capable of handling the demanding conditions of industrial facilities.
Damage caused by static electricity can be expensive and difficult to reverse. Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can ruin finished products, halt production, or even create fire hazards. With KEYENCE static eliminators, industries can protect sensitive electronics, prevent contamination, and keep production lines running smoothly.
Choosing the right static eliminator requires understanding the unique demands of your industry. For large-scale operations, static eliminators with wide ionization coverage are ideal for broader areas. For more targeted applications, like assembly lines or small production spaces, precision models provide the most control and are more efficient. If the line is working in a cleanroom environment or in an area where air circulation and static control are top priority, specialized and customizable units can be designed for these needs.

Static electricity problems can differ in nature depending on the industry or process. We introduce typical static electricity problems in different industries and processes, along with some actual cases of improvement made by introducing ionizers.
Frequently Asked Questions About Static Eliminators / Ionizers
The two commonly known causes of static electricity generation are:
• Objects rubbing against each other (friction)
• Peeling off closely bonded objects (peeling)
Basically, static electricity is generated when objects come into contact and there is a transfer of electrons. Static electricity generated by friction is part of static charge caused by contact and movement. Static electricity caused by peeling off closely bonded objects is caused by the removal of electrons. However, static electricity generated by friction is usually greater than that caused by peeling due to the rubbing at the interface increasing the contact surface and the temperature rise in the surfaces caused by friction.
Dust and particle adherence to metal objects (conductive objects) is caused by charged dust and particles coming near the object and producing electrostatic induction inside the object. Electrostatic induction can also occur when an object is grounded, and therefore, taking direct anti-static measures for metal objects is not effective. For the above reason, it is important that you take anti-static measures against clinging dust and particles. However, static elimination of airborne dust and particles in the open air is realistically impossible. Therefore, the general way to do this is to neutralize the entire space, or in other words, create an environment that can be constantly be neutralized.
Usually, static mats, static flooring, grounding cables, or other methods are used to control static electricity while on the table or bench. As the PCBs leave the bench or table and are transferred into the plastic parts, static elimination can be performed. Ionization during the transfer is an effective method. Eliminating static from the entire room is the most effective for preventing ESD damage. Using an ionizer is one way to eliminate static from the environment.

This guide introduces basic knowledge in detail about static electricity, including how it occurs, different problems caused by static electricity, and how to prevent them. A must-read for anyone who is starting to implement real countermeasures against static electricity.

This document introduces actual examples of anti-static measures taken in the automotive, metal, electronic parts, food, and other industries. A must-read for people working with static electricity problems.

Particle adhesion problems are seen across industries such as semiconductors, LCDs, food and drugs, and automotive. This introduces everything from how particle adhesions occur to how to prevent them, how to remove dust after particle adhesion, and the latest static eliminators.

