Laser Marking Systems / Laser Markers
Proven Laser Solutions for UDI Compliant Stainless Steel Marking
-
Tags:
- Medical , Metal , Laser Annealing
Unique device identification (UDI) compliance is a vital requirement for the integrity of medical devices and the safety of patients. It's key for manufacturers to strictly follow the FDA’s regulations with UDIs to ensure that medical devices are safe for patients, easily traceable, and last a long time. Stainless steel is a common metal used for medical devices, and although it is optimal for use, it has challenges when marking.
To keep compliance with regulations, ensure safety, and keep the purity of stainless steel devices, using laser marking is an optimal choice for marking stainless steel medical devices. Laser markers are user-friendly machines that produce UDI-compliant marks that don’t wear over time or reduce the high corrosion resistance of stainless steel. In this article, we’ll discuss UDI compliance, the challenges of stainless steel, and how laser marking is the solution.
What is UDI Compliance?
In 2013, the FDA passed a regulation requiring manufacturers to label almost all medical devices with a UDI. With the only exempt devices being consumer health products, UDI requirements facilitate traceability practices to make certain that patients are receiving the best care. UDIs store essential device information, like product code, lot number, expiration date, serial number, and manufacturing date. Using a GS1-128 code or a GS1 Data Matrix is standard to store all of this information.

Compliance with the FDA’s UDI system is necessary for manufacturing trustworthy medical devices. When manufacturing, there are key steps you must follow to secure compliance.
- The UDI must appear on the device’s label or package
- The UDI must be readable by a machine and a human
- When a UDI is added, the corresponding device data must be added to the FDA Global Unique Device Identification Database (GUDID)
The Challenges of Marking Stainless Steel
Characteristics like high corrosion resistance, strength, and hygiene make stainless steel an optimal choice for medical devices. Stainless steel’s reliable performance withstanding rounds of sanitation, washing, and use on the body, can’t be beaten.
However, marking on stainless steel is challenging (but necessary). Stainless steel devices are frequently compact, thin, and in non-geometric shapes. Because of this, many manufacturers struggle to mark these devices effectively. Not only is stainless steel’s makeup an issue, but marking it with the wrong tool has detrimental effects.
Ink-based marks quickly disintegrate from the constant washing that stainless steel goes through. And paper-based labels rub off after frequent washing and contaminate patients with paper particles. Lastly, using too much heat on stainless steel reduces its high corrosion resistance.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

How Laser Marking Supports UDI Compliance
UDI compliance is always required – even on the toughest materials. Although stainless steel has challenges, a solution is mandatory. Laser marking medical devices made from steel adequately support UDI compliance by being a permanent, precise, no-surface damage process that works without any adverse results.
High Contrast
UDIs are required to be readable by both machines and humans. If not readable, it eliminates the purpose of a UDI – to store information and give access for quick traceability. When reading a GS1 code, the key to readability is the contrast between black and white to form the design. When using a UV laser, the high absorption rate generates a high contrast mark that makes for a clean pattern.
Precise Marking
High contrast is one characteristic of readability, but precision is also necessary for complying with UDI requirements. An imprecise 2D code can be difficult or impossible for the reader to scan, which defeats the purpose of the UDI mark. The shorter wavelength of UV lasers, 355nm, generates a smaller beam spot making precise marking on complex surfaces achievable.
Permanent Marking
UDI compliance is here to stay, so UDI marks need to be permanent. Laser marking medical devices permanently alter the surface of a device and cannot be removed. Unlike its counterparts like ink-based markers, pad printers, or labels, it is impossible to remove a laser mark even with chemicals, frequent washing, or friction.
No Surface Damage
When staying compliant with UDI requirements, keeping the integrity of the stainless steel device is essential. Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion by itself, but a layer of chromium added to it makes for peak performance. However, using heat on chromium alters it into chromium carbide. The change to chromium carbide is less corrosion resistant, therefore defeating the purpose of the extra layer. Medical device laser marking with a UV laser breaks bonds without heat, hence no surface damage.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.
Achieving UDI Compliance with Laser Marking
Achieving UDI compliance by laser marking medical devices with KEYENCE’s laser markers is quick, user-friendly, and effective. Features like the 3-axis control, 2D code reader, and cold marking make for effective markings.
Cold Marking
Cold marking is the standout reason why achieving UDI compliance with laser marking is so effective. Cold marking refers to the process of using a UV laser and producing minimal heat stress. The laser passes through two crystals, turning from a 1064 nm laser to a 355 nm laser. This laser is thin yet mighty. It has a high absorption rate to mark on any material and a small beam spot to create UDI-compliant codes even in the smallest areas.

Conventional Fiber marking
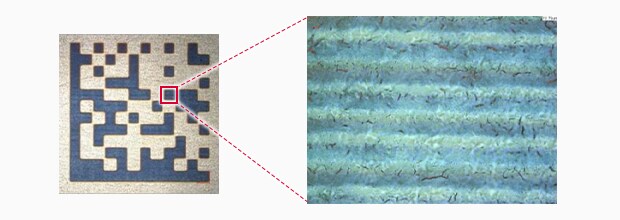
UV Laser marking

Salt water spray test result
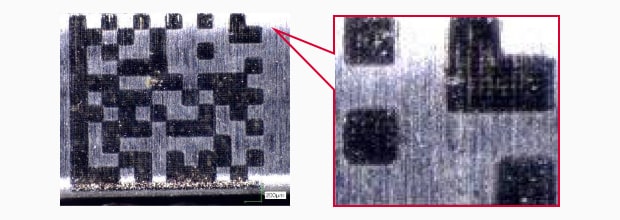
2D Code Reader
The 2D Code Reader is built into the head of the MD-U 3-Axis UV Laser Marker, so it can quickly read and grade the UDI code that has just been marked. Since it is possible to mark and grade the UDI code with the same product, this laser helps to eliminate any mismarked or unmarked parts from being shipped or making their way to the next step in the manufacturing process. This helps to eliminate scrap and provide assurance that the parts being marked are marked accurately and clearly.
3-Axis Control
The 3-Axis control makes for distortion-free marking across even the most complex devices. The marking quality remains the same, even if the target is at the edge or in a circular shape. When marking medical devices, there are odd shapes and sizes, but the 3-axis control ensures that distortion won’t happen.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Related Downloads

This quick guide introduces the basics of metal marking. Learn why different wavelengths matter and discover the various ways laser light interacts with metal parts.

2D codes are used to store date codes, lot codes, serial numbers, and more. Users who are considering 2D code marking should read this laser marking guidebook.









