Industrial Laser Marking Systems / Laser Markers
Direct Part Marking with Laser Marking Systems
-
Tags:
- Laser Marking , Semiconductor , Laser Labeling
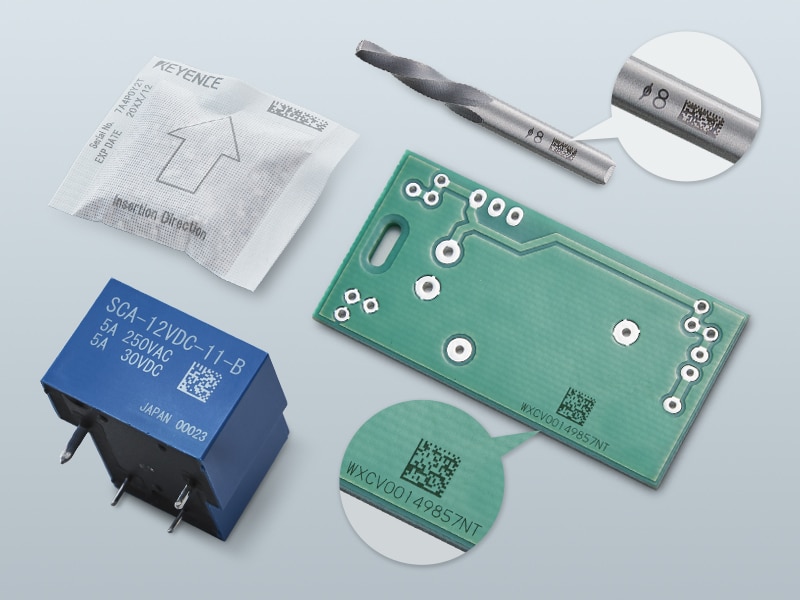
Direct part marking, also known as DPM, is a cornerstone of many aspects of manufacturing. It is the process of creating permanent markings on parts' surfaces. While the process can be adjusted slightly, it most commonly relates to QR codes, data matrix codes, and serial numbers. Below is a brief overview of DPM with laser marking systems.
What is Direct Part Marking?
DPM is a vital component of many industries within manufacturing, and it includes several methods.
Some of these include the following:
- Laser marking
- Screen printing
- Ink stamping
- Engraving
- Tagging
Of all the methods included in the DPM process, laser systems are leading the way in modern innovation.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Advantages of Laser Systems for Direct Part Marking
Direct part marking laser systems are widely sought after in manufacturing as they deliver efficiency, guaranteed permanent markings, and crystal-clear readability.
- Markings at the Start: Unlike many other direct part marking machines, laser systems allow organizations to handle markings at the start of production.
- Permanent results: With more traditional direct part marking methods, permanent markings can be almost impossible to achieve. Laser systems guarantee permanent markings by etching the material.
- Clear readability: Laser-driven direct part marking equipment is easy to read. It offers pristine detail with even the smallest print, and it's bound to stand the test of time.
Direct part marking for manufacturing has numerous applications, but it’s important to recognize that there are different laser marking types to consider.
Challenges in Direct Part Marking and How to Overcome Them
While direct part marking offers many advantages, there are challenges to consider. Not all materials are suitable for laser marking. For example, some materials may reflect the laser or absorb too much heat, causing damage or illegible marks.
Materials like metals, plastics, or ceramics may require specific laser settings. For example, a different wavelength or power laser might be needed to mark certain materials or prevent unwanted issues. In some instances, pre-treatment processes, like surface cleaning or coating, are needed for laser compatibility and quality markings. This can add to the costs and time required to mark the parts themselves.
Another challenge is integrating laser marking systems into existing production lines. On top of that, the cost of equipment can also be an obstacle. While laser marking systems can be a cost-effective solution in the long run, there is an initial investment.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.
Applications of Direct Part Marking Across Industries
Direct part marking with lasers is common across various industries, such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. In the automotive sector, components like engine parts and VINs have direct part mark codes for traceability. Aerospace manufacturers rely on laser marking for parts that are subject to extreme temperatures and pressure (i.e., turbine blades, engine components, and airframe parts).
When it comes to electronics, tiny components like circuit boards benefit from a laser's precise markings. Medical device manufacturers also use laser mark surgical tools and implants for compliance and traceability. Their parts require high readability and permanence that other marking methods do not offer.
Types of Direct Part Marking Equipment
The manufacturing industry has found applications for quite a few types of DPM equipment, and it’s helpful to highlight their core differences. First and foremost, laser marking encompasses several types of laser work.
Of the different types actively used, engraving, oxidizing, etching, and annealing are the most widely used in the manufacturing industry. Laser markers have vast capabilities that have improved the cost and time efficiency of this process.
Newer technologies will emerge in the future, but UV laser markers are at the top of the food chain for many people in this industry. The cold-marking technique prevents heat stress, which has proven extremely valuable for this industry, and the smaller beam spot allows for pristine marks on even the smallest components.
Key Considerations When Choosing a DPM Marking Method
When selecting a direct part marking method or direct part marking machine, several factors should be considered. Material compatibility, mark durability, mark quality, permanence, speed and throughput, cost, integration, and regulatory compliance are a few.
Marking methods differ in how well they work with various materials. For example, laser marking is suitable for most metals, while inkjet printing may be more appropriate for film or paper. When choosing a DPM marking method, be sure that the markings are durable and resistant to abrasion, chemicals, and environmental conditions.
Finally, DPM marking should be able to handle the required throughput and marking speed for your production process. Consider the initial investment, operating costs, and maintenance requirements of different marking methods. The marking system should also be compatible with your existing production equipment and processes.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Comparison of Laser Direct Part Marking Methods
What methods are used for direct part marking? The process has several popular methods, each with its own use case and strengths. The table below highlights key points between different DPM methods.
| Laser Marking Method | Description |
|---|---|
|
Laser Marking Method
|
Description
Used to create machine-readable codes and works best with parts subjected to high abrasion, due to the greater depth of the mark.
|
|
Laser Marking Method
|
Description
This is the fastest process on the list. It melts material quickly and can produce raised or indented marks based on the parameters used. This makes it a great choice for all kinds of metals.
|
|
Laser Marking Method
|
Description
It focuses on creating a chemical reaction underneath the material surface. By dispersing the beam over a larger area, it can create a great contrast with no surface damage to the part.
|
|
Laser Marking Method
|
Description
Utilized for more intensive work with logos, codes, and even character designs.
|
Whether we’re discussing fiber laser markers or hybrid and CO2 designs, each brings a unique benefit to the industry.
Materials Compatible with Laser Direct Part Marking
Part of what makes this process so valuable to manufacturing is its adaptability to a long list of material types. Metal might be a focal point in our day and age, but it goes far beyond this broad category.
Here are a few materials that are compatible with laser DPM:
The list is much bigger than these few, which showcases the importance of the tools behind the process.
Best Practices for Implementing Direct Part Marking in Your Production Process
To successfully add direct part marking into your production process, start by defining your needs. Consider the type of data that will be marked, the materials, and the desired level of readability. Identifying these factors upfront will ensure that the DPM system can meet the specific demands of your application.
The method you choose should be compatible with the materials and meet performance requirements and budget. Be sure to find a system that can seamlessly work with your existing production. If it integrates with your current equipment and software, your organization can avoid potential disruptions.
Another key aspect is how the operators will be trained. Properly train employees to use and maintain the system as intended. Getting them up to speed will reduce the chances of errors or downtime. Finally, maintain and calibrate your DPM direct part marking system as needed. Proper care of the equipment will prevent unwanted issues that could impact production.
Final Thoughts
Direct part marking has changed quite a bit over the years, becoming more efficient and reliable than ever. Moreover, consumers benefit from the quality and longevity of modern marking technology.
To explore how laser systems can aid your manufacturing processes, contact KEYENCE to discuss how our tools can support your organization.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us