KV-X Series × FD-EC Series / FD-EP Series
EtherNet/IP™ Connection Guide
Return to KV Series Connection Guide
KV-X Series × FD-EC Series / FD-EP Series EtherNet/IP™ Connection Guide

FD-EC Series / FD-EP Series

Contents
Step 1 : Devices required for connection
FD-EC Series/FD-EP Series


Step 2 : EtherNet/IP setup for FD-E Series
EtherNet/IP setup for the FD-E Series is configured for NU-EP1.
Two types of NU-EP1 setup methods are available as shown below.
- Setting from the retrieved sensor information
- Setting by manually selecting the sensor
➾ If the actual device is not available at hand, check here.
This manual describes the procedure using the method of "Setting from the retrieved sensor information" that is easy to perform.
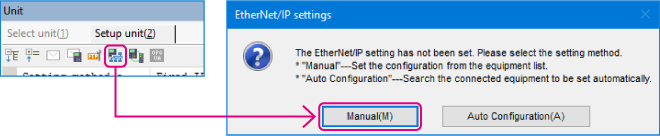
1. Open the Unit Editor of KV STUDIO, and click the EtherNet/IP settings icon. A configuration type selection dialog box is displayed.
Click [Manual (M)].
*Step 2 is performed when a sensor configuration file needs to be imported. If a sensor configuration file has been already imported, connect KV Series and the sensor device via LAN cable, and click [Auto Configuration (A)] before proceeding to Step 3.
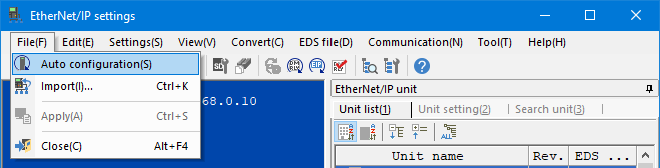
2. With KV Series and the sensor device connected via Ethernet cable, select [File (F)] ⇒ [Auto configuration (S)] on the [EtherNet/IP settings] window.
One point
The following requirements must be satisfied to run the auto configuration.
- NU-EP1 and KV Series are connected with LAN cable.
- Power is supplied to NU-EP1 and KV Series.
- When an Ethernet switch is used, the Ethernet switch is connected to the NU-EP1 and KV Series with LAN cable, and the power is supplied to the Ethernet switch.
3. When the configuration in the Unit Editor differs from that of the actual device, a dialog for confirming transfer of the project is displayed. With the PC and KV Series connected with USB cable, click [Yes (Y)].
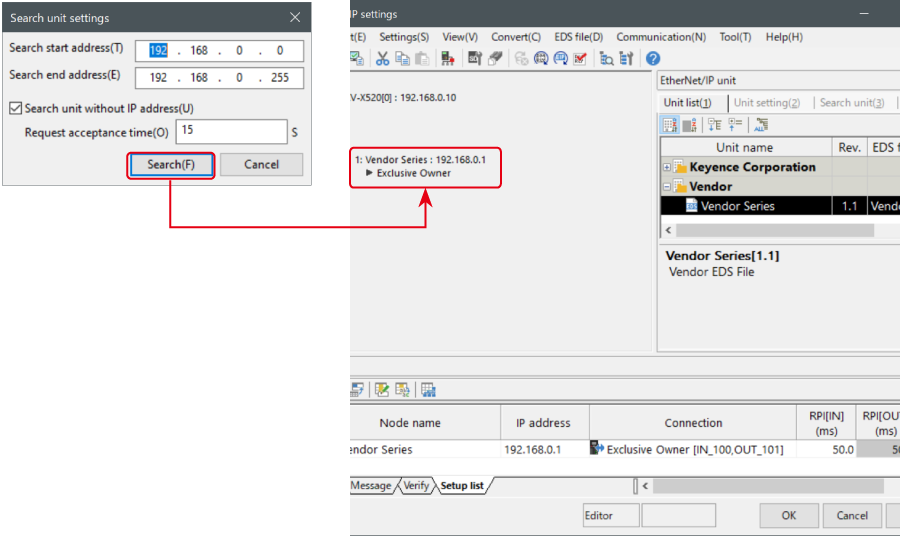
4. When the transfer of the project is completed, the [Search unit settings] dialog is displayed. Then click [Search (F)].
Select the unassigned NU-EP1 from the search results, and click "Unassigned".
The [IP address setting] dialog box is displayed. Then, set the IP address of the NU-EP1 to "192.168.0.1" and click [OK].
*If the IP address has already been assigned, proceed to Step 6.
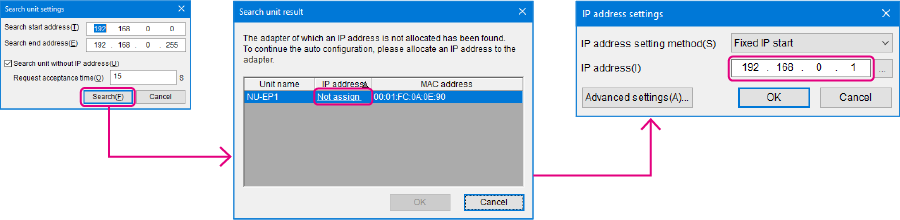
One point
Clicking ![]() in the [IP address setting] dialog box allows IP addresses that have not been used to be searched for.
in the [IP address setting] dialog box allows IP addresses that have not been used to be searched for.
Step 3 : KV-X Series Connection Settings
This section explains how to connect with a fictitious device called "Vendor Series". Replace the "Vender Series" with the device to be connected.
One point
For the KV Series with a CPU function version of 2.0 or later, variables can be assigned to the connection of EtherNet/IP.
When assigning variables to the connection of EtherNet/IP®, check the box of “Displays the variable setting dialog when updating the EtherNet/IP settings (E)” for “Other settings” of “System settings” on the “CPU system settings” dialog.
The “CPU system settings” dialog is displayed by selecting [Display (V)] ⇒ [CPU system settings (P)] from the ”KV STUDIO” menu.
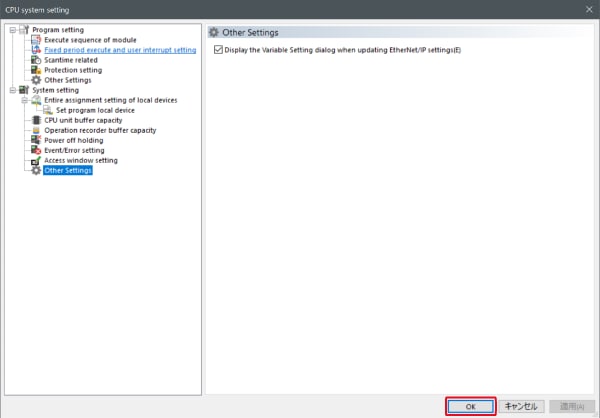
When the box of "Displays the variable setting dialog when updating the EtherNet/IP settings (E)" is checked, at the timing when the EtherNet/IP setting is updated and the changed content of the unit editor is confirmed, a dialog to assign variables to the connection is displayed.
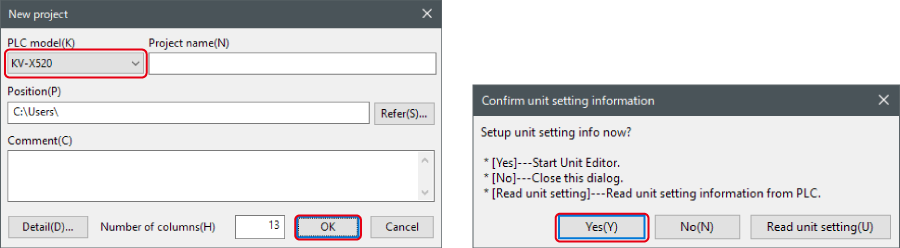
1. Start up the KV STUDIO and create a new project. Set the model option to “KV-X520” and click [OK].
A [Confirm unit configuration setting] dialog box is displayed. Click [Yes (Y)].
2. The unit editor is displayed. On the “Setup unit(2)” tab, click the icon of EtherNet/IP setting. A configuration type selection dialog box is displayed. Click [Manual (M)].
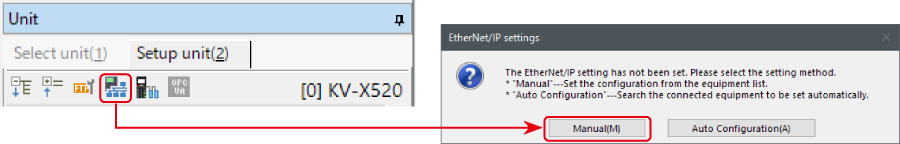
3. On the “Unit setting (2)” tab, set the IP address for KV-X Series. In this example, configure the setting as shown below.
* Step 4 needs to be performed to import a sensor setting file. When the sensor setting file has already been imported, proceed to Step 5.
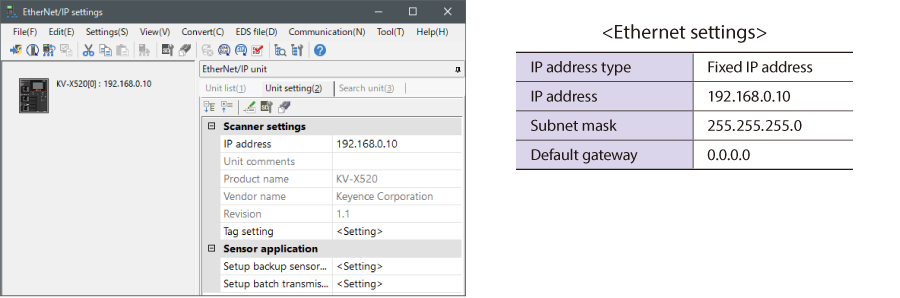
4. Select [EDS file (D)] → [Reg (I)] to import the KEYENCE sensor setting file(ez1 file) or EDS file.
* Download the sensor setting file from the KEYENCE website.
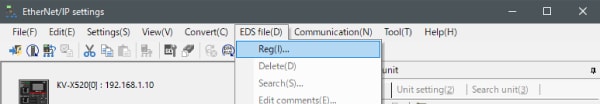
5. With the KV-X Series and the EtherNet/IP devices connected using the Ethernet cable, select [File (F)] → [Auto configuration (S)] on the [EtherNet/IP settings] window.
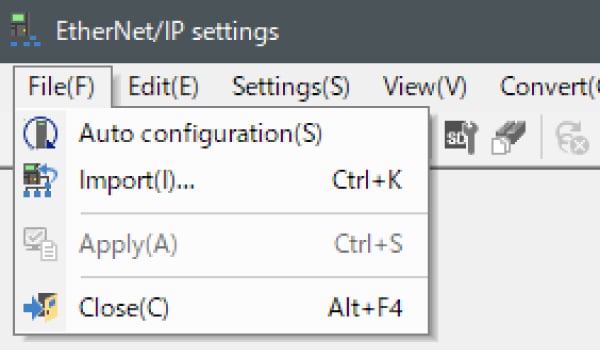
6. When the configuration on the unit editor differs from that of the actual device, a dialog for confirming transfer of the project is displayed. With the PC and KV-X Series connected using the USB cable, click [Yes (Y)].
7. When transfer of the project is completed, the [Search unit settings] dialog is displayed. Then click [Search (F)]. After the auto configuration is completed, "Vendor Series" is automatically registered. Then click [OK] to close the [EtherNet/IP settings] window.
8. Click [OK] on the unit editor to exit.
One point
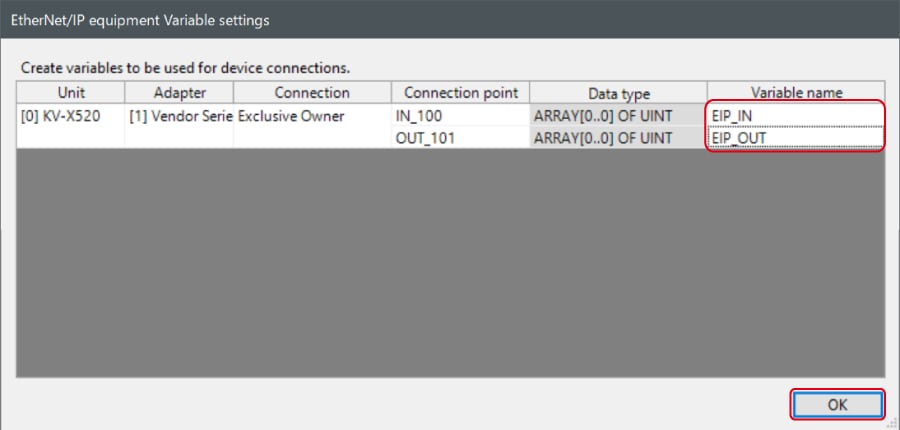
When the box of "Displays the variable setting dialog when updating the EtherNet/IP settings (E)" is checked, the [EtherNet/IP equipment Variable settings] dialog is displayed.
Enter the name of variable assigned to the connection, and click [OK].
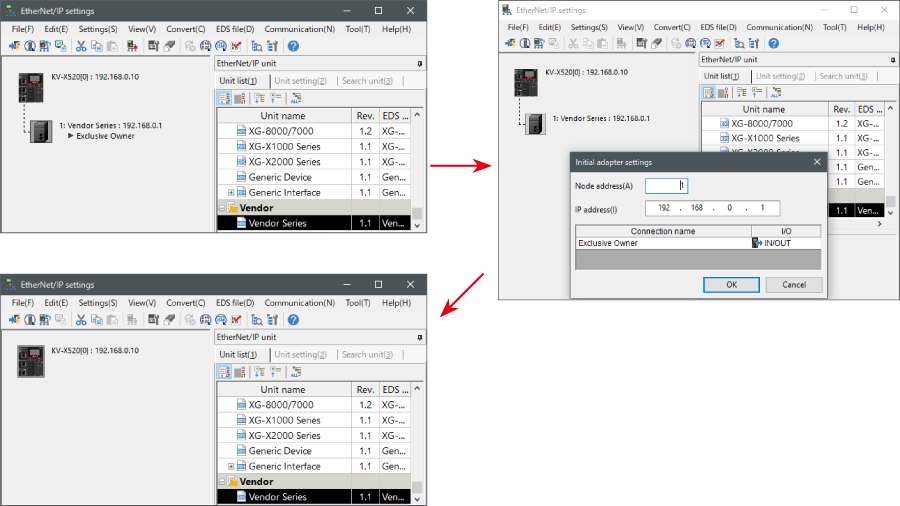
- The way of Device Configuration Settings manually
In the [Unit list (1)] tab of “EtherNet/IP Settings”, drag and drop "Vendor Series" and create a device configuration.
Transferring and Monitoring Setting Data
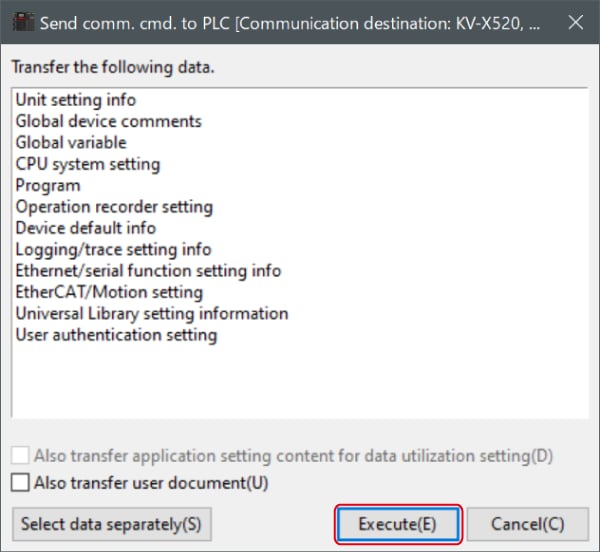
1. From the menu, select [Monitor/Simulator (N)] > [Transfer to PLC (W) → Monitor mode (C)].
In the [Send comm. cmd. to PLC] dialog box, click [Execute(E)].
2. If the following dialog box is displayed before and after transferring the data, click [Yes] both times.
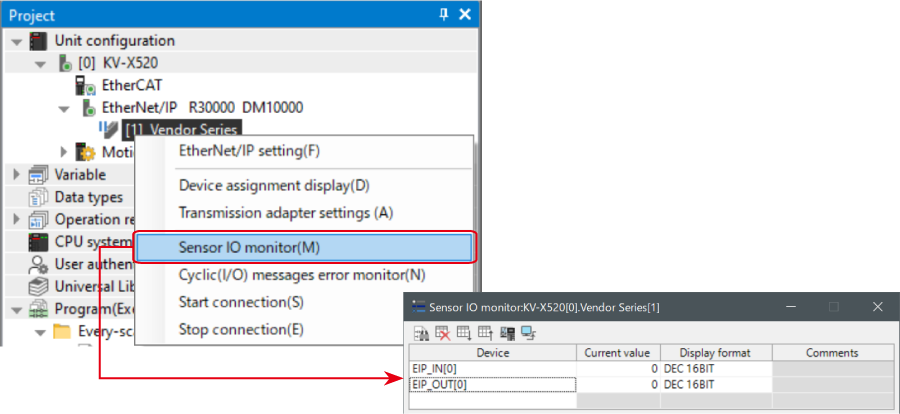
3. Right-click on “Vender Series” in the workspace, and select [Sensor IO monitor (M)].
Scores and other information can be easily monitored.
One point
The information can also be checked on a graph by starting up the real time chart monitor.
Right-click on “Sensor I/O monitor” and select [Real time chart monitor (H)].
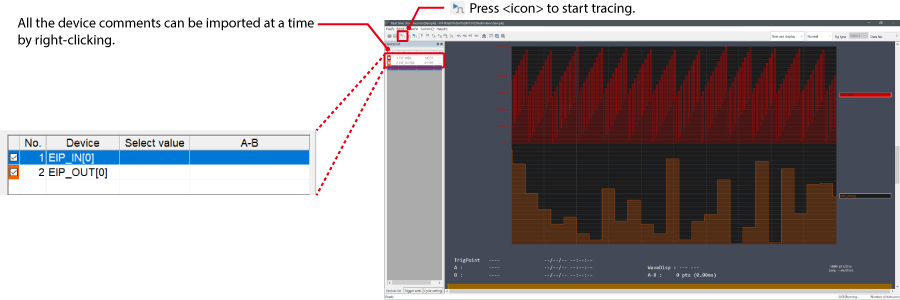
Range adjustment is not required since the real time chart monitor performs scaling automatically.
When Manipulating Parameters with a Program
Changing the Setting Values
The setting values of the sensors can be changed by the following two methods:
A : Change from a PC
B : Change from a ladder program
A : Change from a PC
To change the settings from a PC, use the transmission adapter function in KV STUDIO.
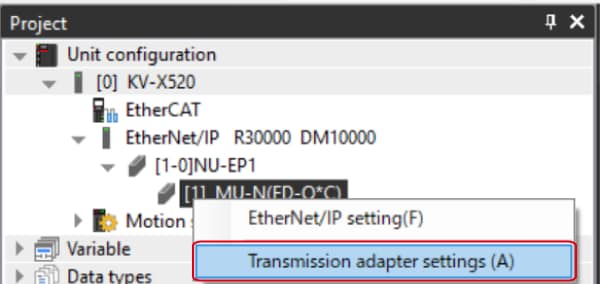
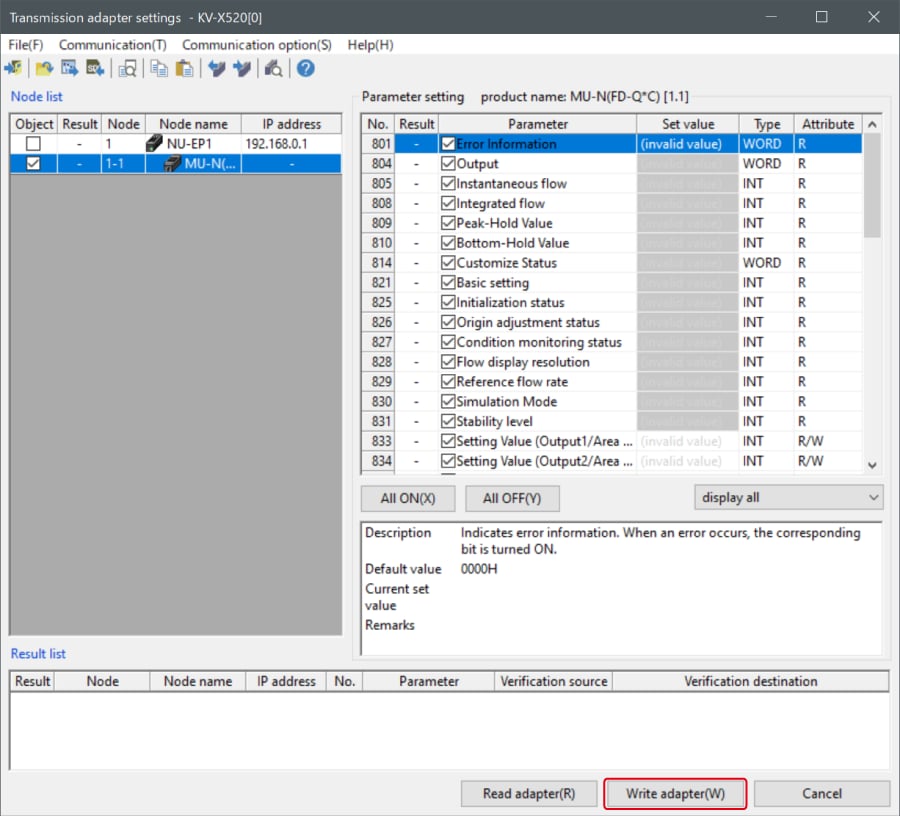
1. Expand the unit configuration in the workspace. Right-click on "Vender Series" and select [Transmission adapter settings (A)].
2. Place a check mark in Setting Value for "Vender Series" and enter the setting value.
Click [Write adapter (W)] to write the setting value to the sensor.
*To read the setting value of a sensor, select [Read adapter (R)].
B : Changed from a ladder program
Use message communication to change the setting values from a ladder program.
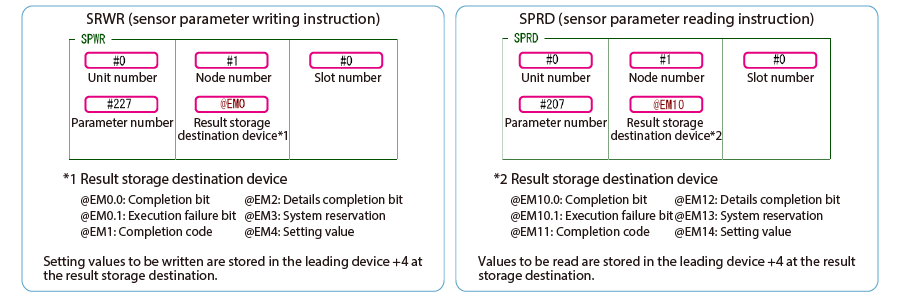
To perform message communication with KV STUDIO, use the sensor setting commands (SPWR [sensor parameter write] and SPRD [sensor parameter read]).
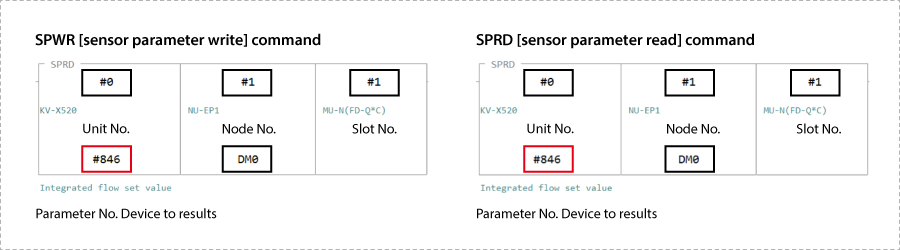
1. In Editor mode, create a ladder program as shown below.
* For the parameter numbers, refer to Parameter list.
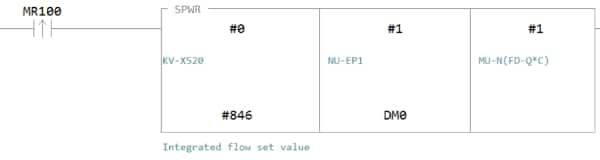
2. Transfer the ladder program.
3. When MR100 is turned on, the setting value is changed.
* Store the setting value in DM4 ([Leading device to store results] + 4).
One point
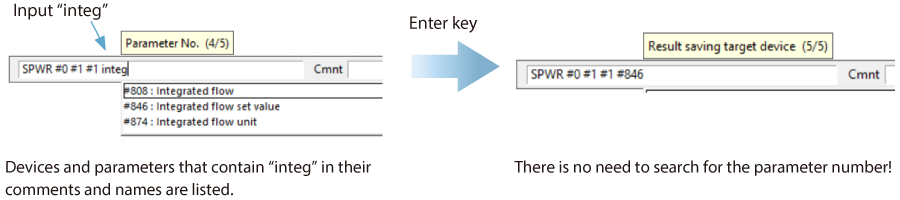
RT (Real-Time) Edit function
When you use a ladder program, you can input device comments or parameter names directly to have input candidates be searched for and displayed automatically.
Extra : Memory mapping
FD-EC Series/FD-EP Series [EtherNet/IP] settings
The following is the list of parameters that can be exchanged in cyclic communication and message communication.
▶ List of parameters that can be obtained in cyclic communication
Since the parameters that can be obtained in cyclic communication are automatically updated between the KV Series and FD-E Series at a fixed internal, a program for reading and writing data is not required. The following is a device map where B000 and W000 are assigned to the leading device of the FD-E Series link devices.
FD-E Series → KV Series
| Member Name | Data Type | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| NU_ErrStatus | BOOL | NU-EP1 Error Status |
| UpdateSensorSetting | BOOL | Updating Sensor Setting |
| SensorEEPROM_Busy | BOOL | Sensor EEPROM Busy |
| SensorExtIn_Busy | BOOL | Sensor External Input Busy |
| SensorSettingErr | BOOL | Sensor Setting Error |
| SensorReady | BOOL | Sensor Ready |
| WarningStatus | BOOL | Warning Status |
| ErrStatus | BOOL | Error Status |
| Error | ARRAY[0..15] OF BOOL | Error |
| Warning | ARRAY[0..15] OF BOOL | Warning |
| OutputCondition | ARRAY[0..15] OF BOOL | L-on/D-on (N.O./N.C.) |
| CurrValOverRange | ARRAY[0..15] OF BOOL | Current Value Over Range |
| CurrValUnderRange | ARRAY[0..15] OF BOOL | Current Value Under Range |
| CurrValInvalid | ARRAY[0..15] OF BOOL | Current Value Invalid |
| Output | ARRAY[0..15] OF BOOL | Output |
| ExtInResp | ARRAY[0..15] OF BOOL | External Input Response |
| ErrID_Number | UINT | Error ID Number |
| ErrCode | UINT | Error Code |
| WarningID_Number | UINT | Warning ID Number |
| WarningCode | UINT | Warning Code |
| SettingErrID_Number | UINT | Setting Error ID Number |
| CurrValue | ARRAY[0..15] OF UINT | Current Value |
| SettingValue1 | ARRAY[0..15] OF UINT | Setting Value 1 |
| SettingValue2 | ARRAY[0..15] OF UINT | Setting Value 2 |
| Reserved | UINT | |
| FastOutput | ARRAY[0..15] OF BOOL | Fast Output |
KV Series → FD-E Series
| Member Name | Data Type | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| ExtInRequest | ARRAY[0..15] OF BOOL | External Input Request |
| Reserved | UINT |
▶ List of parameters that can be obtained in message communication
The message communication is a communication method used when data is exchanged at an arbitrary timing such as change of setting values. The message communication requires a ladder program for communication. However, the KV Series enables communication only by using dedicated instruction words (SPWR/SPRD instruction) for communicating with KEYENCE sensors.
| Attribute ID | Parameter No. | Clamp-on_FD-ECA0 | Dual_FD-EPA0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 800 | - | Number of Group 1 entries | Number of Group 1 entries |
| 801 | 801 | Error information | Error information |
| 802 | - | - | Warning information |
| 803 | - | - | Warning function |
| 804 | 804 | Output | Output |
| 805 | 805 | Current value (Flow) | Current value (Flow) |
| 806 | - | - | Current value (Pressure) |
| 807 | - | - | Current value (Seating) |
| 808 | 808 | Current value (Accumulated) | Current value (Accumulated) |
| 809 | 809 | Peak-hold value (Flow) | Peak-hold value (Flow) |
| 810 | 810 | Bottom-hold value (Flow) | Bottom-hold value (Flow) |
| 811 | - | - | Peak-hold value (Pressure) |
| 812 | - | - | Bottom-hold value (Pressure) |
| 815 | 815 | Slide switch status | Slide switch status |
| 816 | - | - | Application current value 1 |
| 817 | - | - | Application current value 2 |
| 818 | - | - | Application current value 3 |
| 819 | 819 | Diagnostic info | Diagnostic info |
| 824 | 824 | Init settings finished | Init settings finished |
| 825 | 825 | Initialization status | Initialization status |
| 826 | 826 | Flow origin adjustment status | Flow origin adjustment status |
| 827 | - | - | Application learning status |
| 832 | - | Number of Group 2 entries | Number of Group 2 entries |
| 833 | 833 | OUT1 Set/Lower limit val. | OUT1 Set/Lower limit val. |
| 834 | 834 | OUT2 Set/Lower limit val. | OUT2 Set/Lower limit val. |
| 836 | 836 | OUT1 Upper limit val. | OUT1 Upper limit val. |
| 837 | 837 | OUT2 Upper limit val. | OUT2 Upper limit val. |
| 838 | 838 | OUT1 Set/Lower limit val.(Flow) | OUT1 Set/Lower limit val.(Flow) |
| 839 | 839 | OUT2 Set/Lower limit val.(Flow) | OUT2 Set/Lower limit val.(Flow) |
| 840 | 840 | OUT1 Upper limit val. (Flow) | OUT1 Upper limit val. (Flow) |
| 841 | 841 | OUT2 Upper limit val. (Flow) | OUT2 Upper limit val. (Flow) |
| 842 | - | - | OUT1 Set/Lower limit val.(Prs.) |
| 843 | - | - | OUT2 Set/Lower limit val.(Prs.) |
| 844 | - | - | OUT1 Upper limit val. (Prs.) |
| 845 | - | - | OUT2 Upper limit val. (Prs.) |
| 846 | 846 | OUT1 Lower val. (Accumulated) | OUT1 Lower val. (Accumulated) |
| 847 | 847 | OUT1 Upper val. (Accumulated) | OUT1 Upper val. (Accumulated) |
| 848 | 848 | OUT2 Lower val. (Accumulated) | OUT2 Lower val. (Accumulated) |
| 849 | 849 | OUT2 Upper val. (Accumulated) | OUT2 Upper val. (Accumulated) |
| 864 | - | Number of Group 3 entries | Number of Group 3 entries |
| 865 | 865 | Key Lock Status | Key Lock Status |
| 866 | 866 | Key Lock PIN code | Key Lock PIN code |
| 868 | 868 | Output logic | Output logic |
| 869 | 869 | Key Lock Method | Key Lock Method |
| 871 | 871 | Response time (Flow) | Response time (Flow) |
| 872 | - | - | Response time (Pressure) |
| 873 | 873 | Flow unit | Flow unit |
| 874 | - | - | Pressure unit |
| 875 | 875 | Tube material | - |
| 876 | 876 | Select Tube I.D. Setting | - |
| 877 | 877 | Tube inner diameter | - |
| 878 | 878 | Flow direction | Flow direction |
| 879 | 879 | Flow rate span adjustment | Flow rate span adjustment |
| 896 | - | Number of Group 4 entries | Number of Group 4 entries |
| 897 | 897 | OUT1 function | OUT1 function |
| 898 | 898 | OUT2 function | OUT2 function |
| 900 | 900 | OUT1 detection mode | OUT1 detection mode |
| 901 | 901 | OUT2 detection mode | OUT2 detection mode |
| 903 | 903 | IN1 function | IN1 function |
| 904 | - | - | IN2 function |
| 905 | 905 | Pulse weight (Accumulated) | Pulse weight (Accumulated) |
| 906 | 906 | Accumulated flow reset method | Accumulated flow reset method |
| 907 | 907 | Auto hold time | Auto hold time |
| 908 | 908 | Zero cut flow rate | Zero cut flow rate |
| 909 | 909 | Gas type selection | Gas type selection |
| 910 | 910 | Specific heat ratio | Specific heat ratio |
| 911 | 911 | Average molecular weight | Average molecular weight |
| 928 | - | Number of Group 5 entries | Number of Group 5 entries |
| 929 | - | - | OUT1 Set/Lower limit val.(Seat.) |
| 930 | - | - | OUT1 Upper limit val. (Seating) |
| 931 | - | - | Seating pressure lower limit |
| 932 | - | - | Seating pressure upper limit |
| 933 | - | - |
Span adjustment value (seating
confirmation) |
| 935 | 935 | OUT 1 hysteresis(Flow) | OUT 1 hysteresis(Flow) |
| 936 | 936 | OUT 2 hysteresis(Flow) | OUT 2 hysteresis(Flow) |
| 937 | - | - | OUT1 hysteresis (Pressure) |
| 938 | - | - | OUT2 hysteresis (Pressure) |
| 939 | - | - | OUT1 hysteresis (Seating) |
| 943 | - | - | Averaging count |
| 944 | 944 | Simulation mode | Simulation mode |
| 945 | 945 | Simulation value (Flow) | Simulation value (Flow) |
| 946 | - | - | Simulation value (Pressure) |
| 947 | 947 | Blink head LED | Blink head LED |
| 948 | 948 | Zero flow input | Zero flow input |
| 949 | - | - | Application selection |
| 950 | - | - | Application set value 1 |
| 951 | - | - | Application set value 2 |
| 952 | - | - | Application set value 3 |
| 953 | - | - | Application operate setting |
| 955 | - | - | Operate threshold (Flow) |
| 956 | - | - | Operate threshold (Pressure) |
| 957 | - | - | Operate sensitivity |
| 960 | - | Number of Group 6 entries | Number of Group 6 entries |
| 961 | 961 | Flip display | Flip display |
| 962 | 962 | Hold screen display selection | Hold screen display selection |
| 963 | 963 | Indicator mode | Indicator mode |
| 965 | 965 | Display averaging | Display averaging |
| 966 | 966 | Current Display | Current Display |
| 968 | 968 | Display Brightness | Display Brightness |
| 969 | 969 | Display resolution (Flow) | Display resolution (Flow) |
| 970 | 970 |
Display resolution (Accumulated) |
Display resolution (Accumulated) |
| 971 | - | - | Display resolution (Pressure) |
| 975 | 975 | Language | Language |
| 992 | - | Number of Group 7 entries | Number of Group 7 entries |
| 994 | 994 | Tag String | Tag String |
| 1003 | 1003 | Flow conversion | Flow conversion |
| 1004 | 1004 | Reference temperature | Reference temperature |
| 1005 | 1005 | Pressure to use | - |
| 1007 | 1007 | Tuning target | Tuning target |
One point
When SRWR (sensor parameter writing instruction) or SPRD (sensor parameter reading instruction) is executed, a specified sensor parameter is written or read.