Digital Microscopes
Observation and Measurement of Springs Using a Digital Microscope
Like screws, springs are frequently used mechanical components used in various devices such as automobiles, electrical products, and daily necessities.

This section introduces an overview on springs and introduces observation and measurement examples using a digital microscope.
Typical spring types
Coil springs
- Compression coil springs
Compression coil springs generate a repulsive force when loaded in the compression direction. The structure either has an equal pitch or a taper. This type of spring is commonly used as suspension springs in automobiles.

Equal pitch coil spring

Tapered coil spring

Tension coil spring
A : Hooks
- Tension coil springs
Tension coil springs generate a repulsive force when loaded in the extension direction. Hooks are included on both ends of the spring. This type of spring is commonly used in bicycle stands and measuring devices.
- Torsion coil springs
Torsion coil springs generate a repulsive force when the coil is subjected to torsional movement around the spring’s central axis. Hooks may be included on both ends of the spring. This type of spring is commonly used in door locks and hole punches.

Torsion coil spring (with hooks)

Torsion coil spring (without hooks)

Plate springs
- Flat springs
Flat springs are the most common type of plate spring and are often referred to simply as plate springs. This type of spring is commonly used in switches.

- Overlapping plate springs
Overlapping plate springs are made of multiple plate springs of different lengths stacked on top of each other. The more layers that are used, the greater durability the spring will have. This type of spring is commonly used as suspension springs for trucks (also referred to as leaf springs).

Diaphragm spring
- Coned disc springs
Coned disc springs are made by hollowing out the center of a conical plate spring. This type of spring is commonly used as washers to prevent screws from coming loose.

- Spiral springs
Spiral springs are by winding a plate or strip of material into a spiral shape. This type of spring is commonly used in mechanical watches.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Compression coil spring materials and dimensions
Coil spring materials
- Hardened steel wire
This is the least expensive of all metal spring materials and is used in various everyday products.
Symbol : SWC - Piano wire
Offering higher tensile strength than hardened steel wire and greater hardness and fatigue resistance reliability, piano wire is commonly used for industrial springs.
Symbol : SWP - Stainless steel
Stainless steel offers better corrosion and heat resistance than piano wire, making it a mainstay of coil springs.
Symbol : SUS
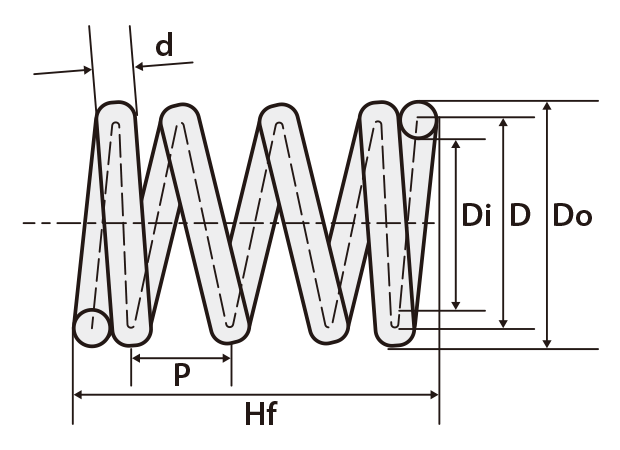
Compression coil spring dimensions
- Dimension description
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The diameter of the wire used for the spring. |
|
|
The average of the outer and inner coil diameters. |
|
|
The diameter of the outer edge of the coil. |
|
|
The diameter of the inner edge of the coil. |
|
|
The height of the spring with no load. |
|
|
The number of coils used by the spring to generate force. |
|
|
The number of all coils between both ends of the spring. |
|
|
The distance between the centers of a helically wound wire. |
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Observation and measurement examples of springs using a digital microscope
The latest examples of observation and measurement of springs using KEYENCE’s VHX Series 4K Digital Microscope are introduced below.
Observation of a coil using depth composition
The depth composition function enables observation of the spring with all coils in focus.
Precision spring depth composition image

VH-Z20, 150×, ring illumination image
Torsion coil spring depth composition image

VH-Z20, 50×, ring illumination image
Observation of wire spring defects

VH-Z20, 50×, ring illumination (normal image)

Image after ring-reflection removal
The ring-reflection removal function enables observation with no glare.
Fractured surface observation image of a spring

VHX-E20, 80×, ring illumination (normal image)

Optical Shadow Effect Mode image
Optical Shadow Effect Mode can be used to visualize detailed surface structures without the need for an SEM.
3D shape measurement image of impacts on a spring

VH-Z20, 200×, ring illumination image
3D shape measurement image of a corroded hole in a spring

ZS-200, 1000×, ring illumination image
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog




