Continuous Inkjet Printers / Case Coder
Process Improvement Examples - Thermal Transfer Overprinter (TTO) vs Continuous Inkjet Printer (CIJ)
In today’s competitive industrial world, companies continue to realize the importance of process improvement to stay ahead of the curve. Printing is one area that often comes under scrutiny, as proper tracking and traceability of manufactured products is a critical business requirement in almost all industries.
Printer Technology - Thermal Transfer Overprinter (TTO) vs Continuous Inkjet Printer (CIJ) - Choosing the Right Solution
Two primary technologies are utilized in the printing industry: thermal transfer overprinting and continuous inkjet printing. Each technology offers various features and advantages, making it necessary to carefully choose the most suitable solution based on their specific requirements. Let's go through each technology in detail.
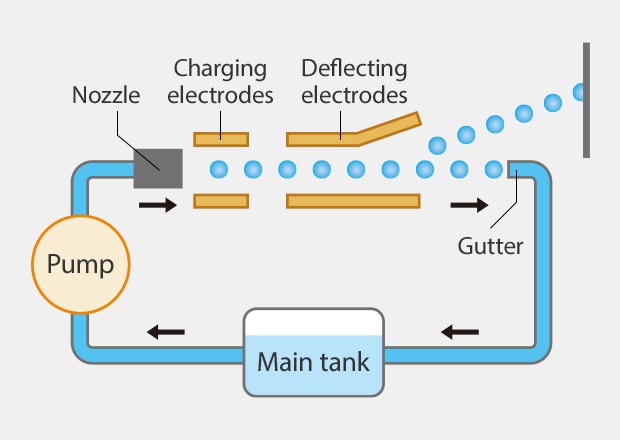
Non contact

Contact
Hot Printer / Thermal Printer Comparison
Hot printers perform printing by placing movable type or the print head in contact with the target. These methods have been commonly used at manufacturing sites and can be installed on automation machines.
This section focuses on the differences between these two contact-type printing methods and non-contact printing methods like inkjet printers. The advantages of non-contact printing are explained below.
Problems with Contact-Type Printers
Contact-type printers use ink ribbons and printing plates. If the ink ribbon jams, the production line must be stopped temporarily. Recovery requires time as the head temperature needs to be heated up, causing significant production downtime. In addition, plate wear and contact pressure must be properly managed.
On the other hand, inkjet printers eliminate the need to use ink ribbons and plates, thereby eliminating all associated problems. Cleaning the print head is as easy as pressing a button. As a result, the daily maintenance required is drastically reduced.
No ink ribbon costs

No head replacement costs

No need for complicated ribbon management
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Comparing Contact-Type Printers to Inkjet Printers
| Contact-type printers | Inkjet printers | |
|---|---|---|
|
Cost
|
Contact-type printers
|
Inkjet printers
|
|
Productivity
|
Contact-type printers
|
Inkjet printers
|
|
Quality
|
Contact-type printers
|
Inkjet printers
|
|
Management
|
Contact-type printers
|
Inkjet printers
|
Curious about our pricing?
Click here to find out more.
Inkjet Printer Application Examples
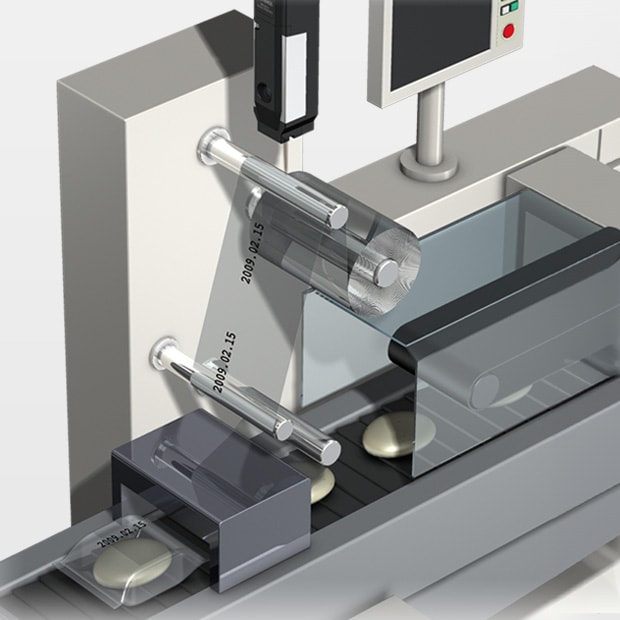
Printing with Pillow-Type Packaging Machines
KEYENCE’s continuous inkjet printers are commonly used for inline printing of date and lot codes during the packaging process. These printers eliminate problems such as blurred or missing prints, as well as holes on films that are usually caused by the contact method printing like stamping.
Through built-in sensors and optimization, flawless and clear marking can be achieved. Inkjet printers can be easily installed on both high-speed production lines or packaging machines. When using encoders with the printers, printing speed is automatically adjusted according to film/line speed to ensure stable printing.
KEYENCE can offer complete proposals including where to install on your existing equipment, how to attach a guide, and when to trigger printing start signals.
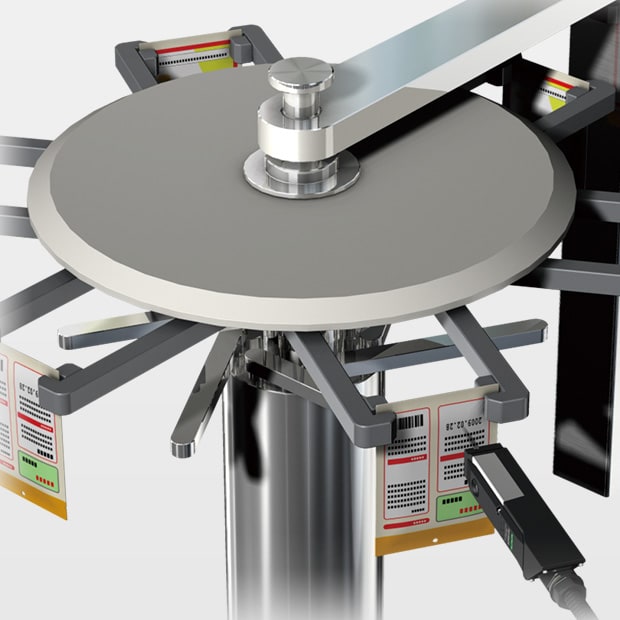
Printing with a Rotary Packaging Machine
Inkjet printers can easily be mounted on the rotary machines that fill pouch containers. By replacing conventional stamp marking with inkjet printing, failures are eliminated such as rubbed print, chipped print, misprints, and packaging damage.
Feel free to contact KEYENCE for more information. We can help address any concerns regarding the printing application, whether it's variations in materials being printed or printing speed.
KEYENCE can offer complete proposals, including where to install it on your existing equipment, how to attach a guide, and when to trigger printing start signals.
Existing content on the page.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.
Thermal Transfer Overprinter (TTO) vs Continuous Inkjet Printer (CIJ) FAQs
When Considering Printing Solutions, What Factors Set Thermal Transfer Overprinter (TTO) and Continuous Inkjet Printers (CIJ) Apart?
TTO and CIJ printers have several distinguishing factors, the primary distinction being the printing technology employed. TTOs utilize a thermal printhead to apply ink from a ribbon composed of wax or resin onto the substrate. Alternatively, TTOs can activate the thermal coating on the substrate itself, resulting in a printed output.
CIJ printers depend on the uninterrupted flow of ink, propelled onto the substrate without any direct contact between the substrate and the printhead. This printing technique exhibits remarkable versatility, enabling printing on a diverse range of materials such as metal, plastic, glass, and the majority of foils and films.
Additional factors to consider are substrate compatibility, operational costs, broader application flexibility, and print speed or product throughput. These are all areas where CIJ printers provide distinct advantages.
In the Thermal Transfer Overprinter vs Continuous Inkjet Comparison, What Are the Primary Benefits of Continuous Inkjet Printers in Manufacturing Settings?
When comparing thermal transfer overprinter vs continuous inkjet printers, the advantages offered by CIJ printers are easily seen. These non-contact printers are ideal for printing on delicate substrates without the risk of damaging the substrate itself.
They’re also compatible with a wider variety of substrate material and shapes compared to TTO printers; they’re considerably faster during operation—printing up to 1,000 meters of single-line text per minute—and often require less maintenance, which translates to higher reliability in the manufacturing process.
Additionally, CIJ printers are incredibly easy to integrate into existing production lines, as they’re often designed to operate in a wide range of environmental conditions with relatively high efficiency.
What Are Examples of Industries Where Printer Technology, Thermal Transfer Overprinter vs Continuous Inkjet, Is Used?
When it comes to using thermal transfer overprinter vs continuous inkjet printers, both are used across a wide range of applications in many industries, with each technology catering to specific needs and the nature of the product that’s being labeled or coded.
For example, the Food and Beverage industry relies on both TTO and CIJ printers for different labeling processes. TTO is mostly used for films or boxes that require large chunks of information, while CIJ is used to print lot codes and date codes on anything from film, bottles, packages, building materials, wire, cable and more in any environment.
Looking to improve your industrial printing? Our MK-G Series CIJ printer is the industry’s first printer with self-troubleshooting. This automated process eliminates the need for user input, allowing your technicians to work on other essential production site needs and ensuring smoother printer operations without any specialized product knowledge or service contracts required.
Contact KEYENCE for more information.
Related Downloads

This guide explains the printing principles and the workflow up to printing by comparing hot foil coders and continuous inkjet (CIJ) printers. Both machines are analyzed from the aspects of productivity, quality, management, and running costs. Tips for solving accidents caused by date coding mistakes are also described.






